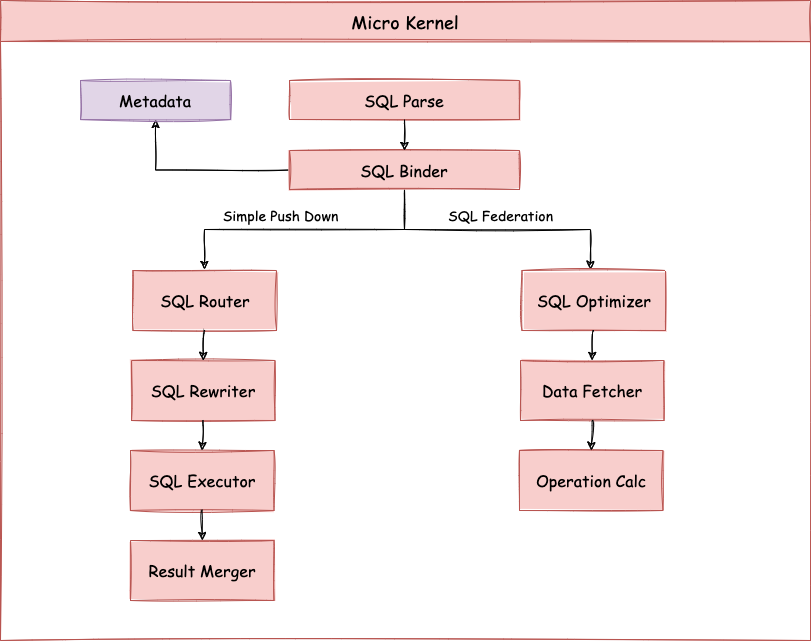
The figure below shows how sharding works. According to whether query and optimization are needed, it can be divided into the Simple Push Down process and SQL Federation execution engine process.
Simple Push Down process consists of SQL parser => SQL binder => SQL router => SQL rewriter => SQL executor => result merger, mainly used to deal with SQL execution in standard sharding scenarios.
SQL Federation execution engine consists of SQL parser => SQL binder => logical optimization => physical optimization => data fetcher => operator calculation.
This process performs logical optimization and physical optimization internally, during which the standard kernel procedure is adopted to route, rewrite, execute and merge the optimized logical SQL.
It is divided into the lexical parser and syntactic parser. SQL is first split into indivisible words through a lexical parser.
The syntactic parser is then used to analyze SQL and ultimately extract the parsing context, which can include tables, options, ordering items, grouping items, aggregation functions, pagination information, query conditions, and placeholders that may be modified.
The sharding strategy configured by the user is matched according to the parsing context and the routing path is generated. Currently, sharding router and broadcast router are supported.
Rewrite SQL into statements that can be executed correctly in a real database. SQL rewriting is divided into rewriting for correctness and rewriting for optimization.
It executes asynchronously through a multithreaded executor.
It merges multiple execution result sets to achieve output through the unified JDBC interface. The result merger includes the stream merger, memory merger and appended merger using decorator mode.
Supported by the experimental Federation Execution Engine, it optimizes complex queries such as associated queries and sub-queries and supports distributed queries across multiple database instances. It internally optimizes query plans using relational algebra to query results through optimal plans.
