Background
The storage and computing ability of stand-alone database is limited. For improving these abilities, ShardingSphere provides sharding capability, which can distribute data across different databases.
For applications that have been running with stand-alone database, there is a problem how to migrate data to sharding data nodes safely and simply.
And for some applications which have used ShardingSphere, the rapid growth of data may also cause a single data node or even the entire data nodes to reach a bottleneck. How to expand their data nodes for ShardingSphere cluster also became a problem.
Introduction
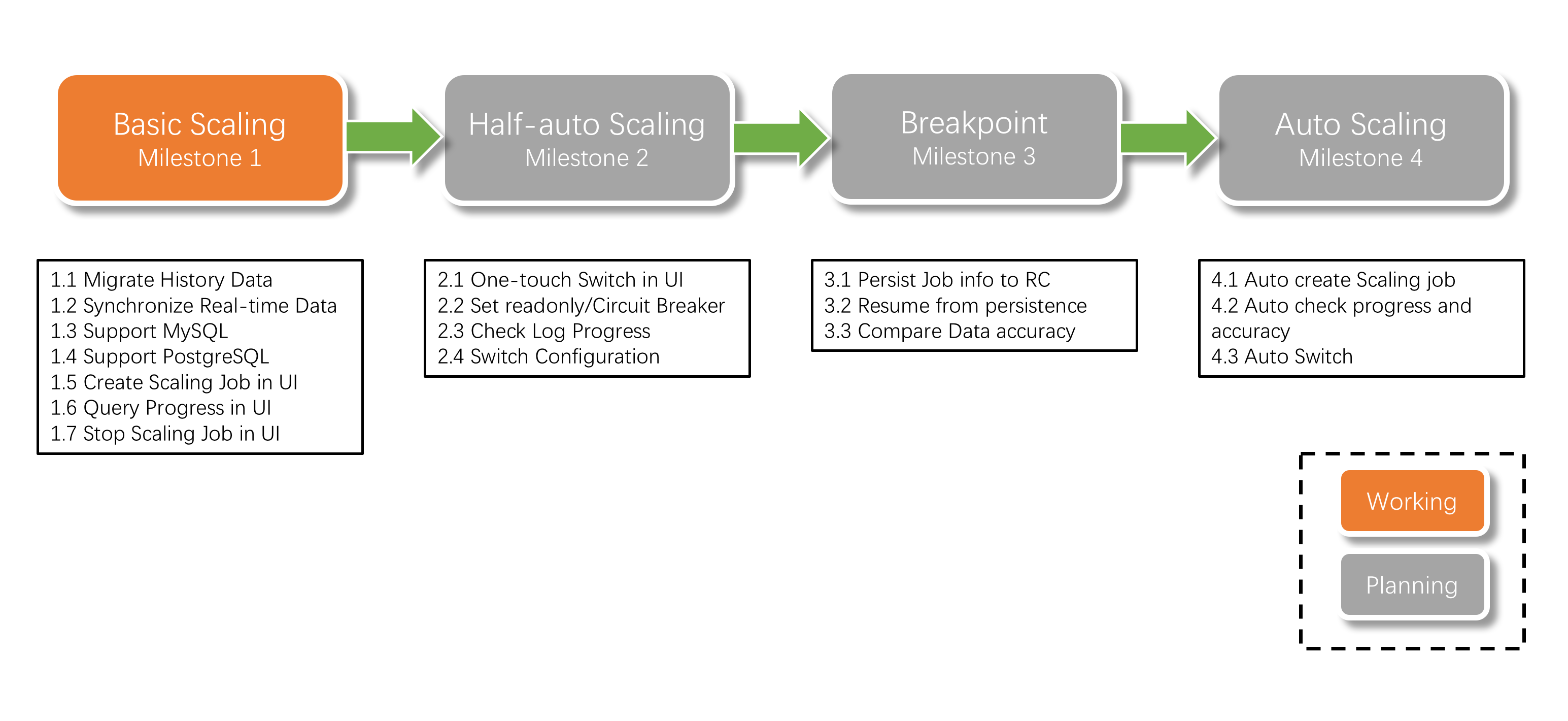
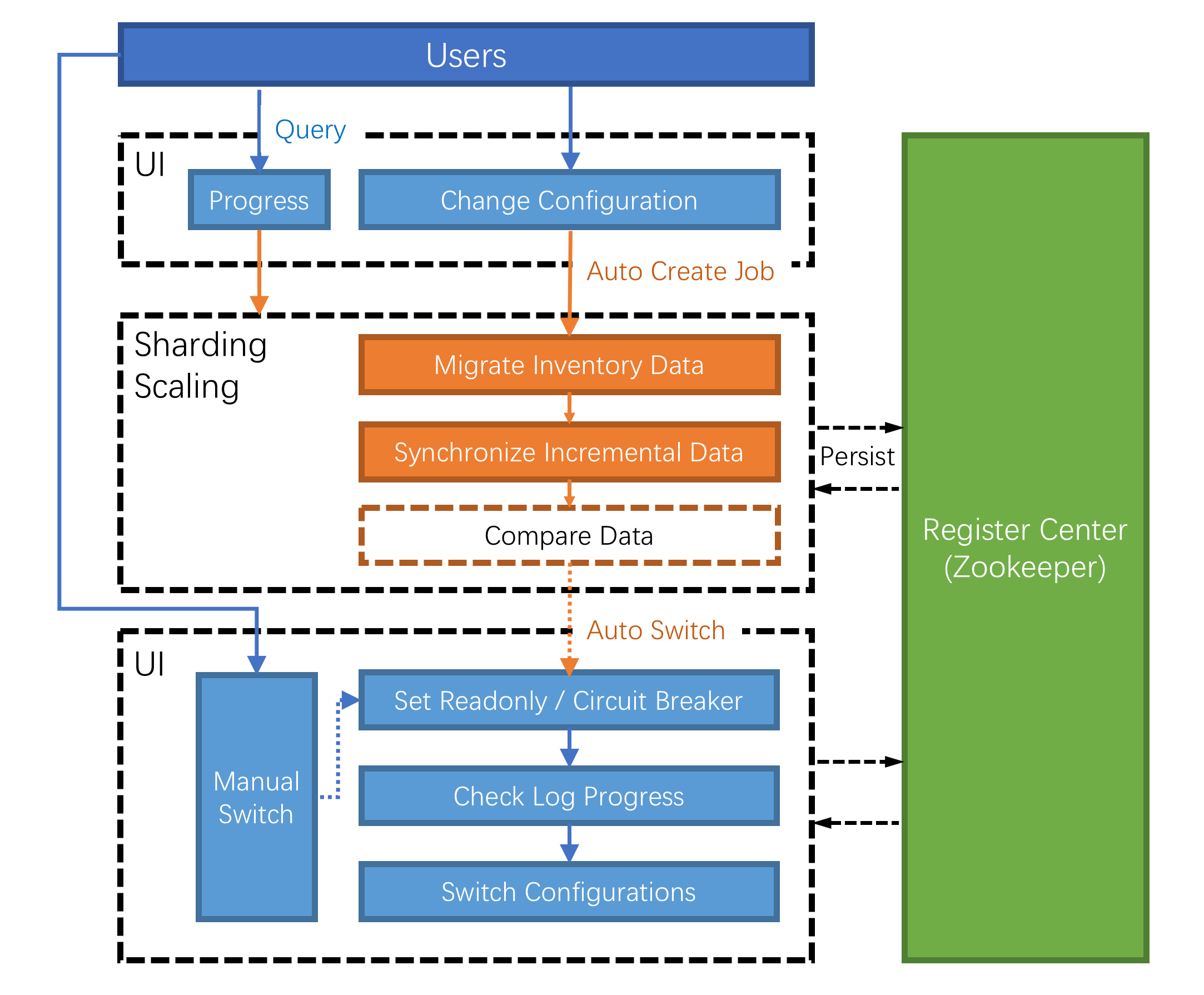
Sharding-Scaling is a common solution for migrating data to ShardingSphere or scaling data in ShardingSphere since 4.1.0.
Challenges
ShardingSphere provides users with great freedom in sharding strategies and algorithms, but it gives a great challenge to scaling. So it’s the first challenge that how to find a way can support kinds of sharding strategies and algorithms and scale data nodes efficiently.
What’s more, During the scaling process, it should not affect the running applications. So It is a other big challenge for scaling to reduce the time window of data unavailability during the scaling as much as possible, or even completely unaware.
Finally, scaling should not affect the existing data. How to ensure the availability and correctness of data is the third challenge of scaling.
Goal
The main design goal of sharding scaling is providing a common ShardingSphere scaling solution which can support kinds of sharding strategies and reduce the impact as much as possible during scaling.
Status
current is in alpha development.