Background
The traditional solution that stores all the data in one single concentrated node has been hard to satisfy the requirement of the massive data scenario of the Internet, no matter in performance, high availability or operation costs.
From the aspect of performance, since the relational database uses the index of B+ tree, when the data amount exceeds the threshold, the deeper index will increase the IO number of disk access, and thereby, weaken the performance of query. In the same time, high concurrency requests also make the centralized database to be the biggest defect of the system.
From the aspect of high availability, stateless service enables scaling out to be at a relatively low cost, which can make all the pressure, at last, fall on the database. But the single data node or the simple master-slave structure has been harder and harder to take these pressures. Therefore, the high availability of the database has become the key of the whole system.
From the aspect of operation costs, when the data in a database instance has reached above the threshold, DBA’s pressure will also increase. The time cost of data backup and recovery will be more uncontrollable with different amount of data. Generally, it is a relatively reasonable range for the data in single database case to be within 1TB.
Under the circumstance that traditional relational databases cannot satisfy the requirement of the Internet, there are more and more attempts to store the data in native distributed NoSQL. But its incompatibility of SQL and imperfection in ecosystem block it from defeating the relational database in the competition, as the relational database still holds an unshakeable position.
Data Sharding refers to splitting the data in one single database and storing them in multiple tables and databases according to some certain standard, so that the performance and availability can be improved. An effective method of data sharding is splitting a relational database into multiple tables and databases, both of which can effectively avoid the query limitation caused by data exceeding affordable threshold. What’s more, database sharding can also effectively disperse TPS. Table sharding though cannot ease the database pressure, can provide possibilities to transfer distributed transactions to local transactions, since cross-database upgrades are once involved, distributed transactions can turn pretty tricky sometimes. The use of multiple master-slave sharding method can effectively avoid the data concentrating on a single node and increase the architecture availability.
Splitting data through database sharding and table sharding is an effective method to deal with high TPS and mass amount data system, because it can keep the data amount lower than threshold and separate the traffic data. Data sharding method can be divided into vertical sharding and horizontal sharding.
Vertical Sharding
According to business sharding method, it is called vertical sharding, or longitudinal sharding, the core concept of which is to specialize databases for different uses. Before sharding, a database is consisting of many data tables corresponding to different businesses. But after sharding, tables are categorized according to business into different databases, and the pressure is also separated into different databases. The diagram below has presented the case in which the user table and the order table are assigned to different databases by vertical sharding according to business need.
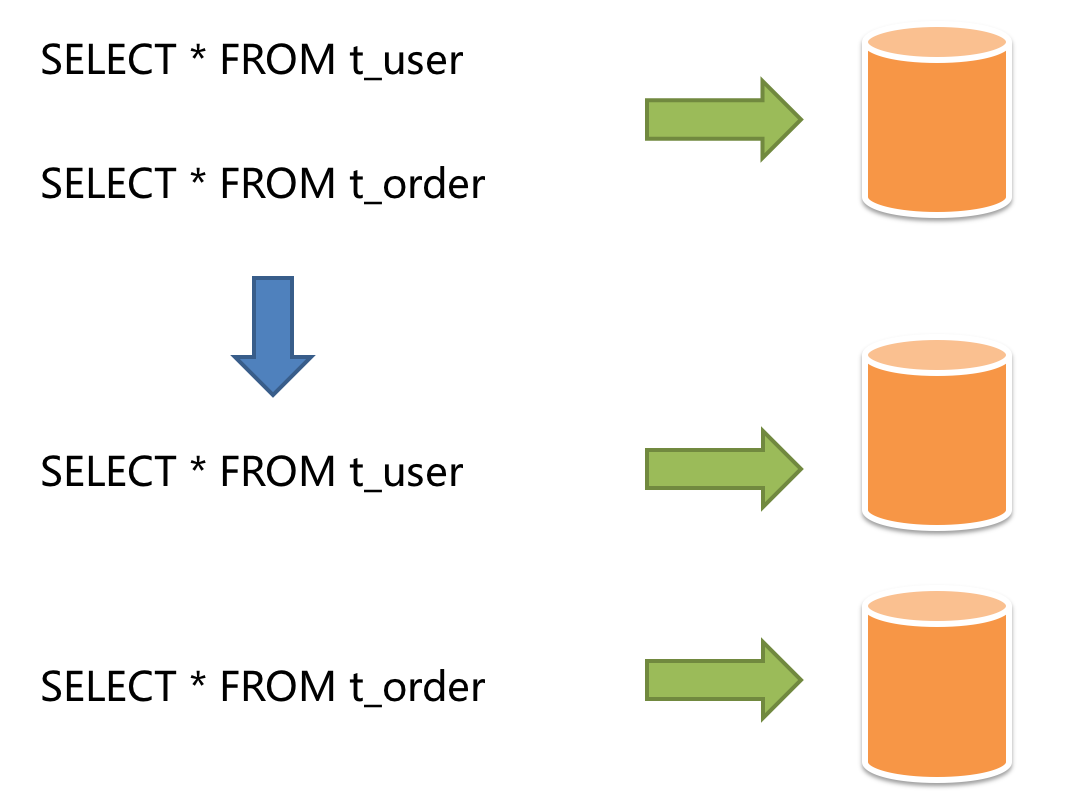
Vertical sharding requires to adjust the architecture and design from time to time, but generally, it is not readily enough to deal with the fast changing Internet business needs and not able to really solve the single-node problem. Sharding of this kind can ease but not completely solve problems brought by the high data amount and concurrency amount. After sharding, if the data amount in the table still exceeds the single node threshold, it should be processed by horizontal sharding.
Horizontal Sharding
Horizontal sharding is also called transverse sharding.
Compared with the categorization method according to business logic of vertical sharding,
horizontal sharding categorizes data to multiple databases or tables according to some certain rules through certain fields, with each sharding containing only part of the data.
For example, according to primary key sharding, even primary keys are put into the 0 database (or table) and odd primary keys are put into the 1 database (or table), illustrated as the following diagram.
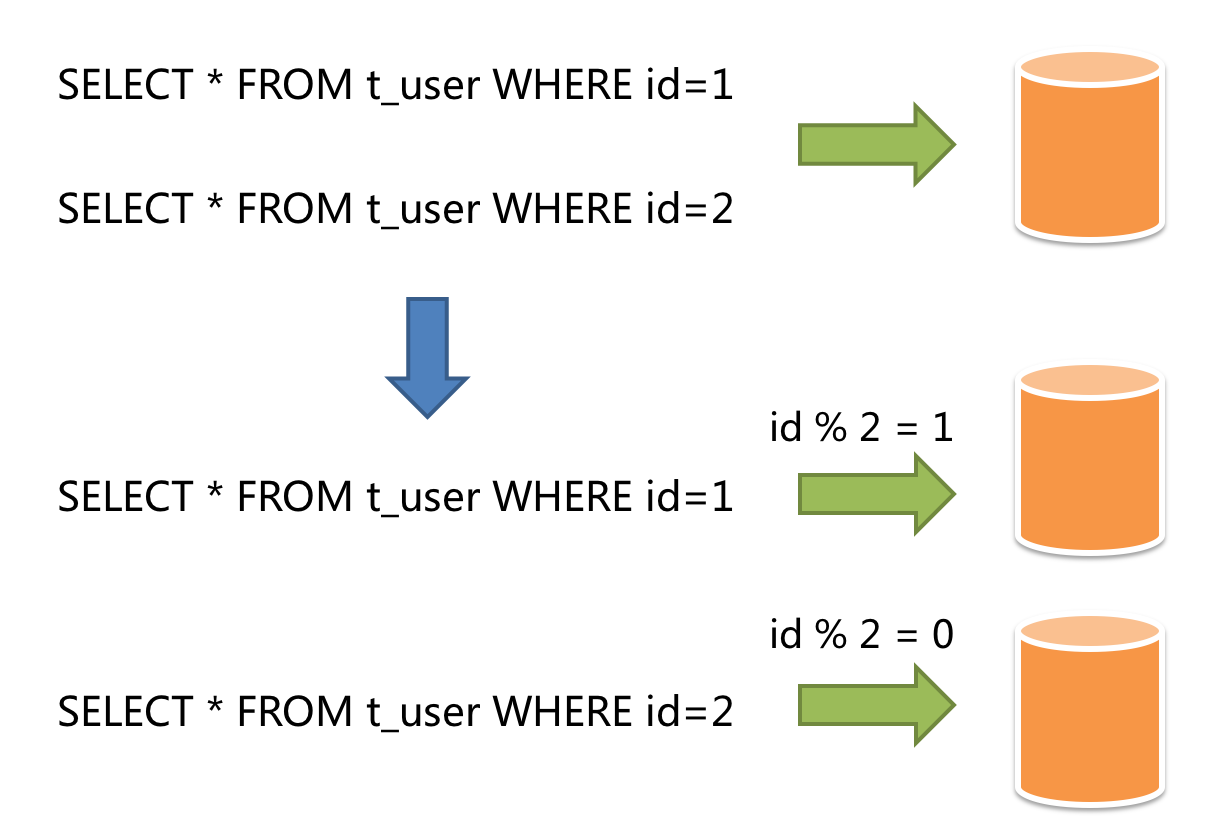
Theoretically, horizontal sharding has overcame the limitation of data processing volume in one single machine and can be extended relatively freely, so it can be taken as a standard solution of database sharding and table sharding.
Challenges
Though data sharding has solved problems such as performance, high availability and single-node backup and recovery, its distributed architecture has also introduced some new problems as acquiring profits.
One is application development engineers and database administrators’ operations become exceptionally laborious, when facing such scattered databases and tables. They should know which exact database table is the one to acquire data from.
Another challenge is that, the SQL that runs rightly in single-node databases may not be right in the sharding database. The change of table name after sharding, or misconducts caused by operations such as pagination, order by or aggregated group by are just the case in point.
Cross-database transaction is also a tricky thing that distributed databases need to deal. Fair use of sharding tables can also lead to the full use of local transactions when single-table data amount decreases. Troubles brought by distributed transactions can be avoided by the wise use of different tables in the same database. In cases that cannot avoid cross-database transactions, some businesses still need transactions to be consistent. Internet giants have not massively adopted XA based distributed transactions since they are not able to ensure its performance in high-concurrency situations. They usually replace strongly consistent transactions with eventually consistent soft state.
Goal
The main design goal of the data sharding modular of ShardingSphere is to try to reduce the influence of database sharding and table sharding, in order to let users use horizontal sharding database group like one database.