Apache ShardingSphere determines the incoming SQL via shadow by parsing the SQL and routing it to the production or shadow database based on the shadow rules set by the user in the configuration file.
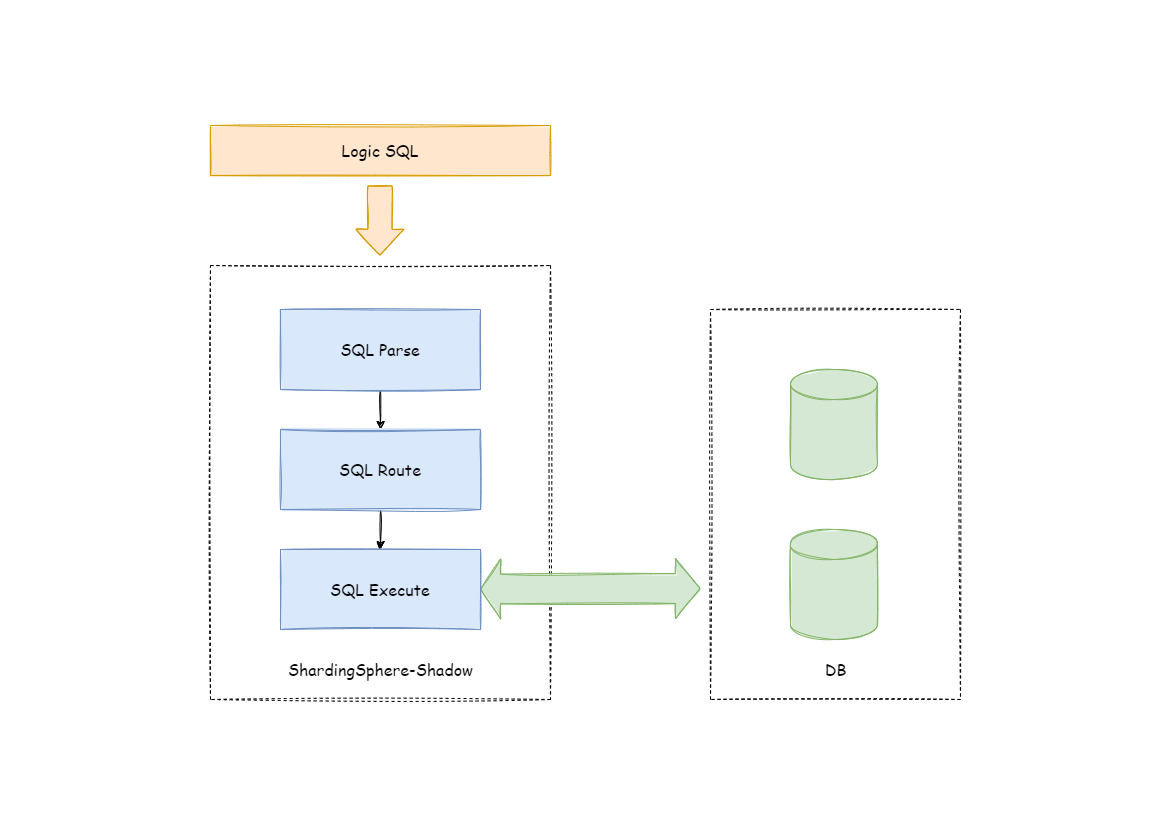
In the example of an INSERT statement, when writing data, Apache ShardingSphere parses the SQL and then constructs a routing chain based on the rules in the configuration file. In the current version, the shadow feature is at the last execution unit in the routing chain, i.e. if other rules exist that require routing, such as sharding, Apache ShardingSphere will first route to a particular database according to the sharding rules, and then run the shadow routing determination process to determine that the execution SQL meets the configuration set by shadow rules. Then data is routed to the corresponding shadow database, while the production data remains unchanged.
Two algorithms are supported. Shadow determination first determines whether the execution SQL-related table intersects with the configured shadow table. If the result is positive, the shadow algorithm within the part of intersection associated with the shadow table will be determined sequentially. If any of the determination is successful, the SQL statement is routed to the shadow library. If there is no intersection or the shadow algorithm determination is unsuccessful, the SQL statement is routed to the production database.
Only supports shadow algorithm with comments attached. In stress testing scenarios, DDL statements are generally not required for testing, and are used mainly when initializing or modifying shadow tables in the shadow database. The shadow determination will first determine whether the execution SQL contains comments or not. If the result is a yes, the HINT shadow algorithm configured in the shadow rules determines them in order. The SQL statement is routed to the shadow database if any of the determinations are successful. If the execution SQL does not contain comments or the HINT shadow algorithm determination is unsuccessful, the SQL statements are routed to the production database.
JAVA API: shadow database configuration
YAMLconfiguration: shadow database
Spring Boot Starter: shadow database configuration
Spring namespace: shadow database configuration
