After years of stagnation, ElasticJob is back with the first Apache version 3.0.0-alpha
Within a few months ElasticJob as the subproject of Apache ShardingSphere has fixed and merged 535 issues and pull requests. More importantly, the ElasticJob community released the first official version: 3.0.0-alpha after joined Apache Software Foundation.
Background
ElasticJob (https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere-elasticjob) is a distributed scheduling solution for internet ecology and massive tasks. ElasticJob consisting of two separate subprojects, ElasticJob-Lite and ElasticJob-Cloud. It was born in 2015, at that time the industry had outstanding job scheduling library such as QuartZ, but lacked of exploration at distributed field. The lack of distributed scheduling cloud platform products has caused ElasticJob to attract attention from the beginning. It effectively makes up for the shortcomings of operations in the distributed field, and provides a one-stop automated operation and maintenance management and control terminal. Each product uses a unified operation API. Developers only need to develop once and deploy at will.
In the technology selection for ElasticJob, it chose to stand on the shoulders of giants instead of reinvent the wheel. It perfectly combines the standard job scheduling library QuartZ, and ZooKeeper, a weapon for distributed coordination, to quickly and stably build a new concept of distributed scheduling framework.
ElasticJob scheduling model
The scheduling model of ElasticJob is divided into in-process scheduling ElasticJob-Lite, which supports thread-level scheduling, and ElasticJob-Cloud, which supports process-level scheduling.
In-process scheduling
ElasticJob-Lite is a thread-level scheduling framework for in-process. It can be used in conjunction with Java frameworks such as Spring, Dubbo and Spring-injected Beans can be used freely in operations, such as data source connection pools, Dubbo remote services, etc. It fits business development well and make development more conveniently.
ElasticJob-Lite is deployed with business applications, and its life cycle is same as the business applications. It is a typical embedded lightweight architecture. ElasticJob-Lite is very suitable for ordinary Java applications with stable resource usage and simple deployment architecture. It can be understood as a Java development framework.
ElasticJob-Lite itself is a non-centralized architecture and does not require an independent centralized scheduling node. Each task node under the distributed system is a self-scheduled scheduling job in a timely manner. Only one registry is needed between tasks to coordinate task status in distributed scenarios, ZooKeeper is supported as a registry currently.
The architecture diagram is shown below:
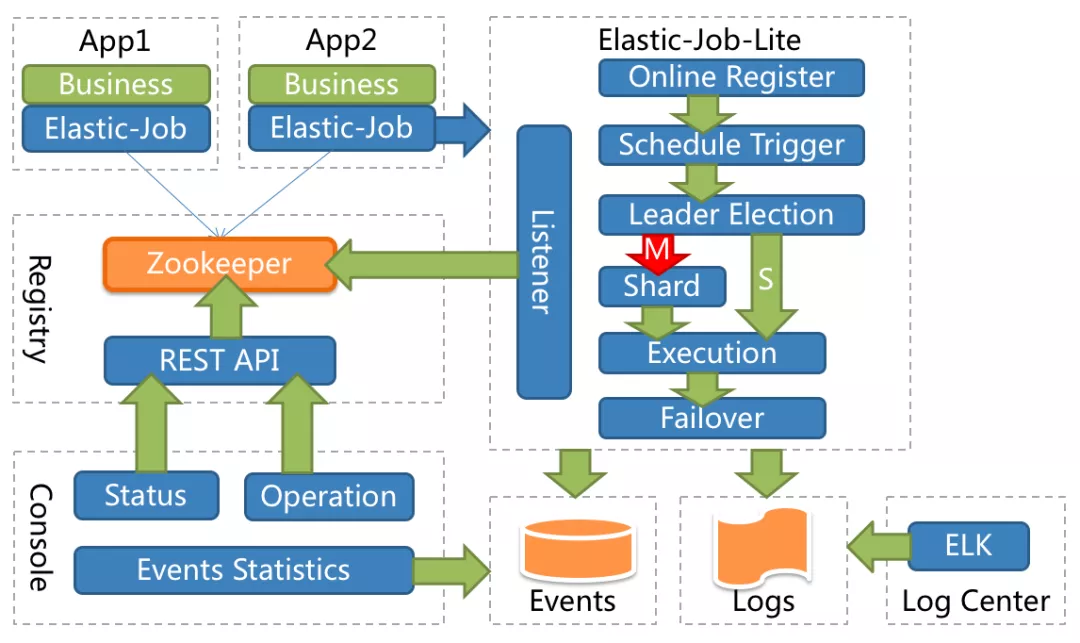
It can be seen from the figure that the distributed job node of ElasticJob-Lite obtains the master node through election, and shards through the master node. After the fragmentation is completed, the master node and the replica node are the same, and both execute tasks in a self-scheduled manner.
Process level scheduling
ElasticJob-Cloud has two methods: in-process scheduling and process-level scheduling. Since ElasticJob-Cloud can control the resources of the job server, its job types can be divided into permanent tasks and transient tasks. Resident tasks like ElasticJob-Lite, which is in-process scheduling has completely different instantaneous tasks. It makes full use of the peak-clipping and valley-filling capabilities of resource allocation. It is process-level scheduling, each task starts a new process.
ElasticJob-Cloud needs to control resources through Mesos, and allocate tasks and resources through the scheduler deployed in Mesos Master. Cloud adopts a centralized architecture to transfer the high availability of the dispatch center to Mesos.
Its architecture diagram is shown below:
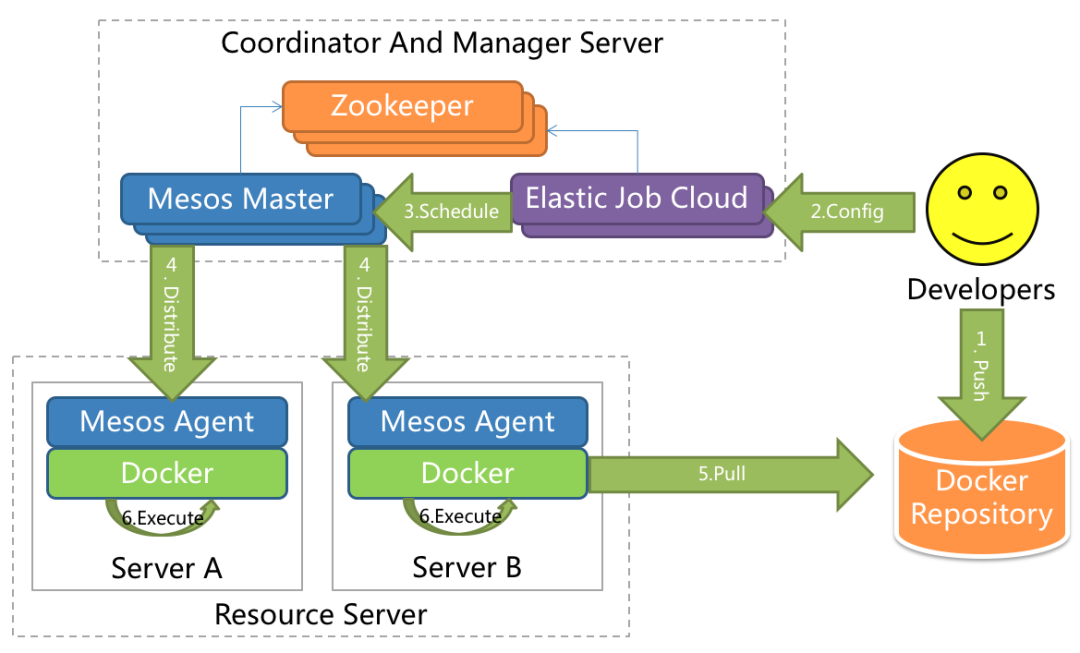
It can be seen from the figure that ElasticJob-Cloud not only has all the capabilities of Lite, but also has the ability to allocate resources and distribute tasks. It fully manages a series of life cycles of job development, packaging, distribution, scheduling, governance, and sharding. It is a true job cloud scheduling system.
Compared with the simplicity and ease of use of ElasticJob-Lite, ElasticJob-Cloud’s strong dependence on Mesos increases the complexity of system deployment, making it more suitable for large-scale operating systems.
Function list
ElasticJob functions mainly include flexible scheduling, resource allocation, job management, and visual control.
Flexible scheduling
Elastic scheduling is the most important function of ElasticJob, and it is also the origin of the product name. It is a task processing system that allows tasks to be scaled horizontally through sharding.
The concept of task sharding items in ElasticJob enables tasks to run in a distributed environment, and each task server only runs the shards assigned to that server. With the increase or downtime of servers, ElasticJob will sense the changes in the number of servers in near real-time, thus it could re-allocate more reasonable task fragmentation items for distributed task servers, so that tasks can increase efficiency as resources increase.
Resource allocation
Scheduling refers to assigning suitable resources to tasks at suitable times and making them effective. ElasticJob has the ability to allocate resources, it can schedule tasks like a distributed operating system. Resource allocation is realized by Mesos. Mesos is responsible for allocating the required resources (CPU and memory) declared by the task and isolating the allocated resources. ElasticJob will execute the task after obtaining the resource.
Considering the relatively complex deployment of the Mesos system, ElasticJob split this part into the ElasticJob cloud for advanced users. With the strong development of Kubernetes, ElasticJob will also complete the connection of the Cloud part with it in the future.
Job governance
Governance and coordination of high availability, failover, and re-execution of missed jobs in distributed scenarios.
Visual control terminal
Mainly include operation life cycle management and control, execution history query, configuration center management, etc.
3.0.0-alpha features a sneak peek
Build & dependencies
-
Upgrade to Java 8
-
Upgrade the minimum supported ZooKeeper version to 3.6.x
API changes
-
Change the groupId of Maven coordinates to org.apache.shardingsphere.elasticjob
-
Change the package name to org.apache.shardingsphere.elasticjob
-
Change the Spring namespace name to http://shardingsphere.apache.org/schema/elasticjob
-
Brand new job API, you can use SPI to customize job types
-
Use SPI to reference configuration strategies, such as task fragmentation, thread pool usage, and error handling strategies
-
Separate the console code from the job core module
New function
-
Multiple schedulers, adding one-time task scheduler
-
Provide the official Spring Boot Starter of the ElasticJob-Lite project
-
Support the use of multiple database types to store job history track data
-
Allow users to specify a suitable IP address through environment variables
-
Brand new console interface
3.x version design interpretation
It can be seen from the Release Notes that ElasticJob 3.x is not a patched version of 2.x, but a set of new products implemented through innovative design concepts.
The most intuitive change in ElasticJob 3.x is to split the original single-digit number of modules into dozens of micro-modules with responsibilities for cleaning up.
The keywords of the new version are microkernel, scalability and ecological docking.
Microkernel
ElasticJob 3.x abstracts API and infrastructure modules, and separates all modules such as registry, historical execution trajectory, console, job executor, Lite and Cloud.
The height of kernel module is extensible, but does not rely on the implementation of the extensible module itself. It inherits the previous capabilities of ElasticJob, while continuing to provide developers with a toolkit of distributed services, while opening up a scaffolding that can be freely customized and extended to developers.
Scalable
ElasticJob 3.x defines a wealth of extensible interfaces on the basis of the microkernel, including extensible interfaces such as job types, configuration strategies, historical execution trajectory storage, and registry storage to be done.
Developers can weave customized functions without modifying the ElasticJob source code, which is truly closed for modification and open for extension.
**Ecological docking **
ElasticJob 3.x provides the official Spring Boot Starter, and has started to develop automatic probes based on Apache SkyWalking, making it more convenient to integrate into the existing technology system.
In addition, what can be read from the Release Notes is that ElasticJob 3.x has not significantly updated Cloud, and its main changes are concentrated in the kernel and Lite modules.
For Mesos, which is complex to deploy, it is no longer popular. ElasticJob 3.x will gradually weaken its dependence on it, and plans to provide more generalized resource isolation APIs in the future, so that the Cloud product line can be connected to Mesos, Kubernetes, and even independent independent Deployment and use.
3.0.0-beta feature preview
After adjusting the project and package structure, ElasticJob 3.0.0-beta will focus on the development of new functions and standardization of operational APIs.
New feature preview
- Job dependency
Supports job dependency based on directed acyclic graph (DAG). Dependency includes dependencies based on the overall dimensions of the job, as well as dependencies based on job shards, to create a more flexible job governance solution.
- HTTP job type
Support HTTP job type, and provide another cross-language job type besides Script.
Operation API standardization
-
Provide a unified API interface based on RESTful operations
-
Simplify SDK-based operation API interface
Future plan
In the future, ElasticJob will keep moving forward. The main plans are as follows:
Scheduling execution separation
Completely separate the scheduler and executor. The scheduler can be deployed together with the executor, which is a decentralized lightweight version of ElasticJob lite; the scheduler can be deployed separately from the executor, which is a one-stop distributed scheduling system for ElasticJob cloud resource management and control.
To be a Cloud management products that are easier to use
The ElasticJob cloud, which currently only supports Mesos, is built into a job cloud management platform that supports Mesos and Kubernetes, and provides a pure job management and control platform that can be used independently without Mesos and Kubernetes without resource control.
Pluggable ecology
In the same vein as Apache ShardingSphere, ElasticJob will also provide a more pluggable and modular architecture to provide developers with infrastructure. It is convenient for developers to develop secondary development based on ElasticJob and add various customized functions, including but not limited to job types (such as big data jobs, HTTP jobs, etc.), registry types (such as Eureka, etc.), execution track storage media (such as Other database types) etc.
ElasticJob will eventually make Lite and Cloud available to development engineers and operation and maintenance engineers in a closer way, sharing their scheduling, execution, and job libraries. The overall plan is as follows:
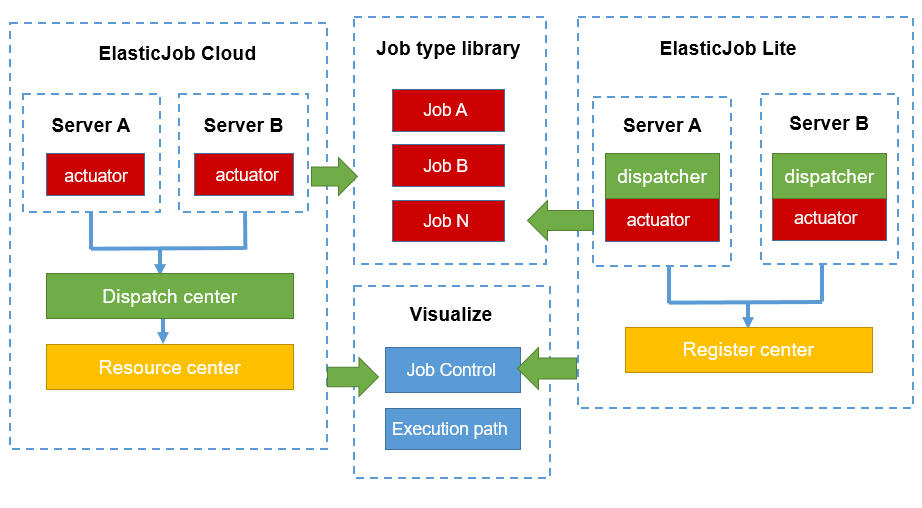
About the ElasticJob community
The ElasticJob community has stagnated in the previous few years, mainly because the author’s personal energy is limited and snowed under with work. After receiving the demand for the scheduling infrastructure for the flexible migration of Apache ShardingSphere, the ElasticJob community decided to restart and continued to shine as a sub-project of Apache ShardingSphere. The current ElasticJob has officially moved the project source code into Apache’s GitHub repository, and has been very active in the months since the restart, and is on the GitHub weekly and monthly trend rankings.
ElasticJob is a sub-project of Apache ShardingSphere (https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere). The goal is to become an independent top-level Apache project and provide the cornerstone of data scheduling for the elastic migration of Apache ShardingSphere.
About the Author
Zhang Liang, JD Digital Technology Center Architecture Expert, Apache ShardingSphere PMC Chair.
Love open source, be good at Java-based distributed architecture, and respect elegant code.
At present, the main energy is devoted to building the distributed database middleware Apache ShardingSphere into the industry’s first-class financial-grade data solution.
Apache ShardingSphere (https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere) is the first top-level project of the Apache Software Foundation led by JD. It is also the first distributed database middleware of the Apache Software Foundation.
Published the book “Future Architecture-From Servicing to Cloud Native”.
GitHub: https://github.com/terrymanu, technical exchanges and corrections are always welcome.