Principle
Overall Architecture
Apache ShardingSphere makes shadow judgments on incoming SQL by parsing SQL, according to the shadow rules set by the user in the configuration file, route to production DB or shadow DB.
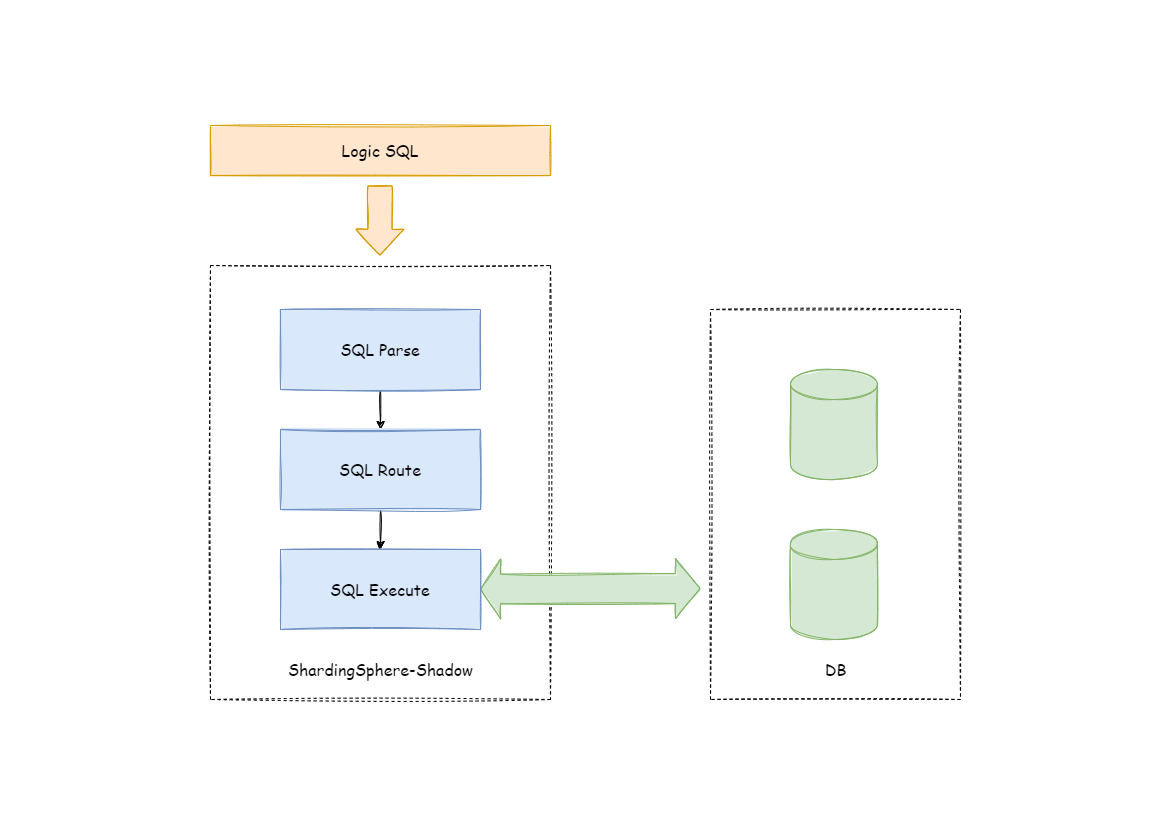
Shadow Rule
Shadow rules include shadow data source mapping, shadow tables, and shadow algorithms.
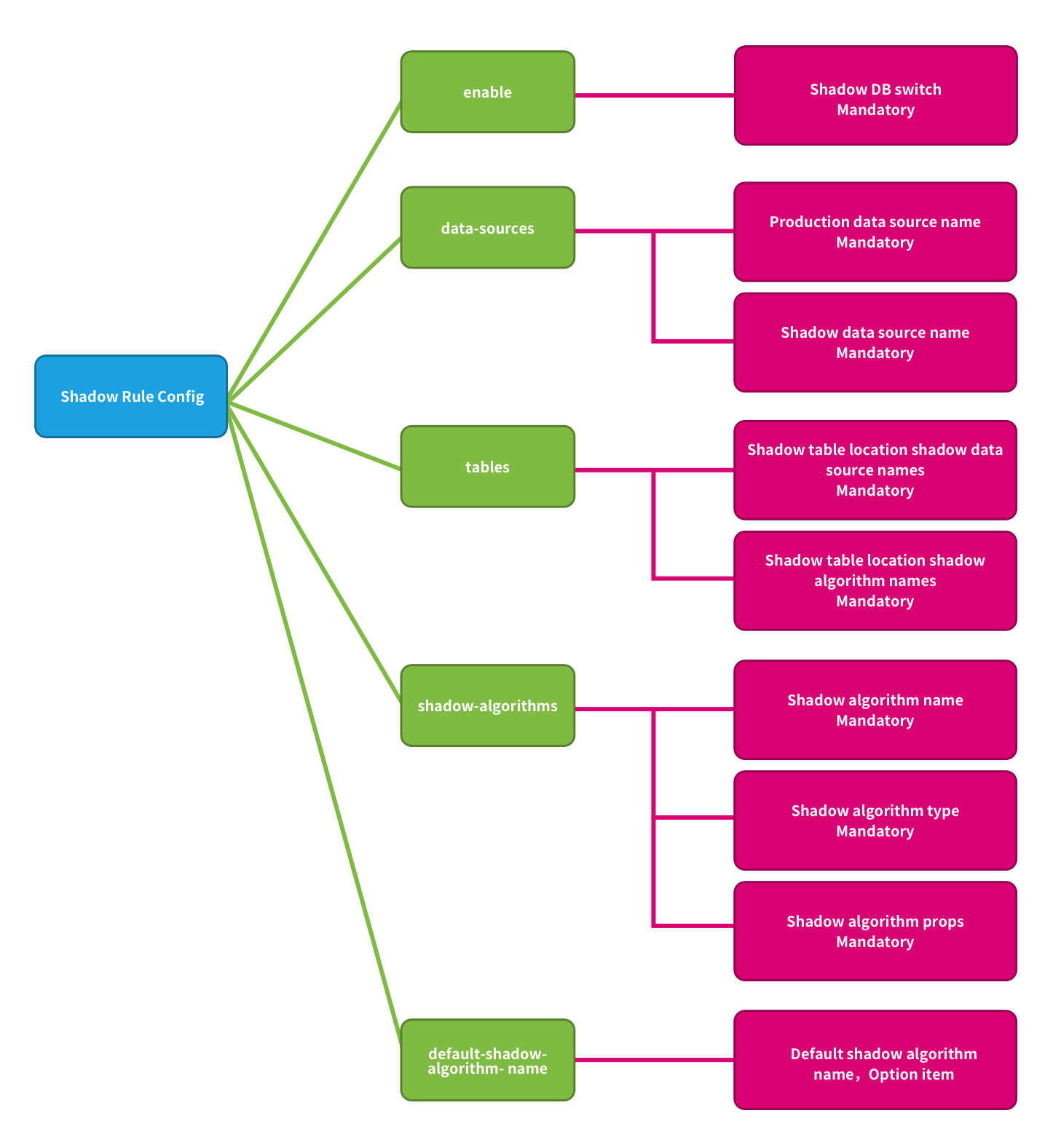
enable:Shadow DB switch, The default value is false. Optional value true/false.
data-sources:Production data source name and shadow data source name mappings.
tables:For tables related to stress testing, shadow tables must be included in the shadow library. The shadow table needs to specify the corresponding shadow library mapping and shadow algorithm.
shadow-algorithms:SQL routing shadow algorithm.
Routing Process
Take the INSERT statement as an example, When writing data, Apache ShardingSphere will parse the SQL, and then construct a routing chain according to the rules in the configuration file.
In the current version of the function, the shadow function is the last execution unit in the routing chain, that is, if there are other rules that require routing, such as sharding, Apache ShardingSphere will first route to a certain database according to the sharding rules, and then perform the shadow routing decision process.
It is determined that the execution of SQL satisfies the configuration of the shadow rule, the data is routed to the corresponding shadow database, and the production data remains unchanged.
Shadow Judgment Process
When the shadow library switch is turned on, a shadow judgment will be made on the executed SQL statement.
Shadow judgment currently supports two types of algorithms, and users can choose one or combine them according to actual business needs.
DML Statement
Support two shadow algorithms.
The shadow judgment first judges whether the table associated with the SQL execution has an intersection with the shadow table.
If there is an intersection, the shadow algorithm associated with the shadow table of the intersection is determined in turn.
If any of the shadow algorithms associated with the shadow table succeeds, the SQL statement is routed to the shadow database.
If there is no intersection or the shadow algorithm is unsuccessful, the SQL statement is routed to the production database.
DDL Statement
Only support note shadow algorithm.
Generally, there is no stress test on DDL statements. It is mainly used for the initialization of the shadow library environment or the adjustment of the shadow table.
The shadow determination will first determine whether the executed SQL contains annotations, and if it contains annotations, the shadow algorithm of the annotations in the shadow rule will be determined in turn.
If any one of the annotation shadow algorithms succeeds, the SQL statement is routed to the shadow library.
No SQL does not contain annotations or the annotation shadow algorithm is unsuccessful and is routed to the production database.
Shadow Algorithm
Shadow algorithm details, See the List of built-in shadow algorithms
Use Example
TODO