Integrating SCTL into RAL
Integrating SCTL into RAL
In the previous article “An Introduction to DistSQL” written by Haoran Meng, the Apache ShardingSphere Committer shared the motivating reasons behind the design of DistSQL, explained its syntax system, and impressively showcased how you can use one SQL to create a sharding table.
Recently, the ShardingSphere community has redesigned the SCTL grammar and the execution engine, integrating SCTL into the DistSQL syntax system. Now RAL contains the old SCTL function, making ShardingSphere’s command language even more convenient for database management. Today, our community author would like to introduce the changes and elaborate on how you can use the new RAL command lines. We always pursue better user experience, and the upgrade we developed this time is just another typical example.
Review: What’s RAL?
RAL is a subtype of DistSQL. DistSQL contains three types: RDL, RQL and RAL.
-
Resource & Rule Definition Language (RDL):to create, modify or delete resources and rules.
-
Resource & Rule Query Language (RQL): to query and display resources and rules.
-
Resource & Rule Administration Language (RAL): to control senior functions of resources and rules management.
What’s SCTL?
ShardingSphere Control Language (SCTL) is the command language of Apache ShardingSphere to execute a series of operations on enhanced features such as Hint, transaction type switch and sharding execution query.
SCTL is made of the below commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| sctl:set transaction_type=XX | Change the transaction type ( LOCAL, XA, or BASE), e.g. sctl:set transaction_type=XA. |
| sctl:show transaction_type | Query the transaction type. |
| sctl:show cached_connections | Query the numbuer of physical database cached connections. |
| sctl:explain SQL | Query the execution plan of the logic SQL, e.g. sctl:explain select * from t_order; |
| sctl:hint set PRIMARY_ONLY=true | For the current connection only. Choose whether to hint at the primary database. |
| sctl:hint set DatabaseShardingValue=yy | For the current connection only. The Hint setting only works for database sharding. Add the database sharding value yy. |
| sctl:hint addDatabaseShardingValue xx=yy | For the current connection. Add database sharding value yy to the logical table xx. |
| sctl:hint addTableShardingValue xx=yy | For the current connection. Add table sharding value yy to the logical table xx. |
| sctl:hint clear | For the current connection only. Clear all hint setting. |
| sctl:hint show status | For the current connection only. Query hint status: primary_only:true/false, sharding_type:databases_only/databases_tables |
| sctl:hint show table status | For the current connection only. Query hint database sharding value of the logical table. |
Why Integrate SCTL Now?
-
The SCTL feature was released in ShardingSphere v3.1.0. At that time, we did not even create the DistSQL concept - now DistSQL can provide the new API with enriched features and consistent concepts. To avoid an excessively steep learning curve, we chose to integrate SCTL into RAL.
-
SCTL syntax is actually very easy to identify: it is marked with the special prefix “sctl:”. Instead of using our Parser engine, parsing a SCTL command relies on string matching. Now that DistSQL is mature enough, it’s time to delete these special codes and let the Parser engine handle them.
-
Additionally, SCTL syntax is not real SQL. Apache ShardingSphere 5.0.0 has just been released, and DistSQL is already the best solution to manage resources and rules. This SQL created by ShardingSphere is truly SQL in practice - so why not integrate SCTL into DistSQL?
Analysis
Our community has discussed at length on how to handle the change. Finally, we decided to replace SCTL syntax with new RAL commands (see the table below):
| Before | After |
|---|---|
| sctl:set transaction_type=XX | set variable transaction_type=XX |
| sctl:show transaction_type | show variable transaction_type |
| sctl:show cached_connections | show variable cached_connections |
| sctl:explain SQL | preview SQL |
| sctl:hint set PRIMARY_ONLY=true | set readwrite_splitting hint source = [auto / write] |
| sctl:hint set DatabaseShardingValue=yy | set sharding hint database_value = yy; |
| sctl:hint addDatabaseShardingValue xx=yy | add sharding hint database_value xx= yy; |
| sctl:hint addTableShardingValue xx=yy | add sharding hint table_value xx = yy |
| sctl:hint clear | clear [hint / sharding hint / readwrite_splitting hint] |
| sctl:hint show status | how [sharding / readwrite_splitting] hint status |
| sctl:hint show table status | Catagorized into 【show sharding hint status】 |
Now, Let’s analyze these commands one by one:
show variable transaction_type
Query the current transaction type.
Input command
mysql> show variable transaction_type;
Output
+------------------+
| TRANSACTION_TYPE |
+------------------+
| LOCAL |
+------------------+
set variable transaction_type
Modify the current transaction type (LOCAL, XA, or BASE; case insensitive).
Input command
mysql> set variable transaction_type=XA;
Output
a. If successful, display “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Execute show variable transaction_type again and the type is XA now.
show variable cached_connection
Query how many physical database cached connections.
Input command
mysql> show variable cached_connections;
Output
+--------------------+
| CACHED_CONNECTIONS |
+--------------------+
| 0 |
+--------------------+
preview SQL
Preview the actual SQL. Here, we give an example in read-write splitting scenario. ShardingSphere supports previewing any SQL commands.
Input command
mysql> preview select * from t_order;
Output
+-----------------+----------------------------------------------+
| datasource_name | sql |
+-----------------+----------------------------------------------+
| read_ds_0 | select * from t_order ORDER BY order_id ASC |
| read_ds_1 | select * from t_order ORDER BY order_id ASC |
+-----------------+----------------------------------------------+
Note:This is an Hint example in read-write splitting scenario. We configure two rules: read-write splitting and sharding. The configuration is the following:
rules:
- !READWRITE_SPLITTING
dataSourceGroups:
ds_0:
writeDataSourceName: write_ds_0
readDataSourceNames:
- read_ds_0
ds_1:
writeDataSourceName: write_ds_1
readDataSourceNames:
- read_ds_1
- !SHARDING
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
standard:
shardingColumn: user_id
shardingAlgorithmName: database_inline
defaultTableStrategy:
none:
shardingAlgorithms:
database_inline:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: ds_${user_id % 2}
show readwrite_splitting hint status
For the current connection only. Query hint status of readwrite_splitting.
Input command
mysql> show readwrite_splitting hint status;
Output
+--------+
| source |
+--------+
| auto |
+--------+
set readwrite_splitting hint source
For the current connection only. Set read-write splitting hint strategy (AUTO or WRITE). Supported source types include:AUTO and WRITE (case insensitive) .
- AUTO: automated readwrite-splitting hint
- WRITE:compulsory hint at the master library
Input command
mysql> set readwrite_splitting hint source=write;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Re-execute show readwrite_splitting hint status; show the ource is changed into Write;
c. Execute preview select * from t_orderand see the queried SQL will go to the master database.
mysql> preview select * from t_order;
+-----------------+----------------------------------------------+
| datasource_name | sql |
+-----------------+----------------------------------------------+
| write_ds_0 | select * from t_order ORDER BY order_id ASC |
| write_ds_1 | select * from t_order ORDER BY order_id ASC |
+-----------------+----------------------------------------------+
clear readwrite_splitting hint
For the current connection only. Clear the read-write splitting hint setting.
Input command
mysql> clear readwrite_splitting hint;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Recover default of readwrite_splitting hint; use show readwrite_splitting hint status command to see the result.
Note:Here is another sharding example for Hint. Hint algorithm is used for both database sharding and table sharding. The sharding configuration rules are shown below:
rules:
- !SHARDING
tables:
t_order_item:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}
databaseStrategy:
hint:
shardingAlgorithmName: database_inline
tableStrategy:
hint:
shardingAlgorithmName: table_inline
shardingAlgorithms:
database_inline:
type: HINT_INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: ds_${Integer.valueOf(value) % 2}
table_inline:
type: HINT_INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: t_order_item_${Integer.valueOf(value) % 2}
show sharding hint status
For the current connection only. Query sharding hint status.
Input command
mysql> show sharding hint status;
Output
The initial status output is :

Verify the hint and input the command:
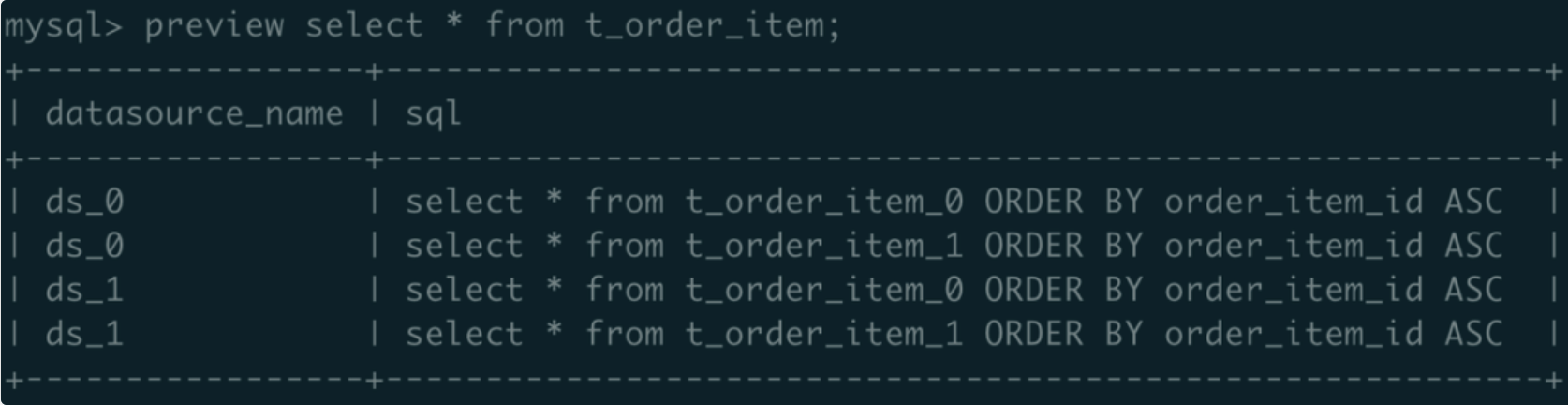
preview select * from t_order_item;
Output No hint value now. Query is fully dependent on the hint.
-set sharding hint database_value;
For the current connection only. Set the Hint as for database sharding only, and add database value=1.
Input command
mysql> set sharding hint database_value = 1;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
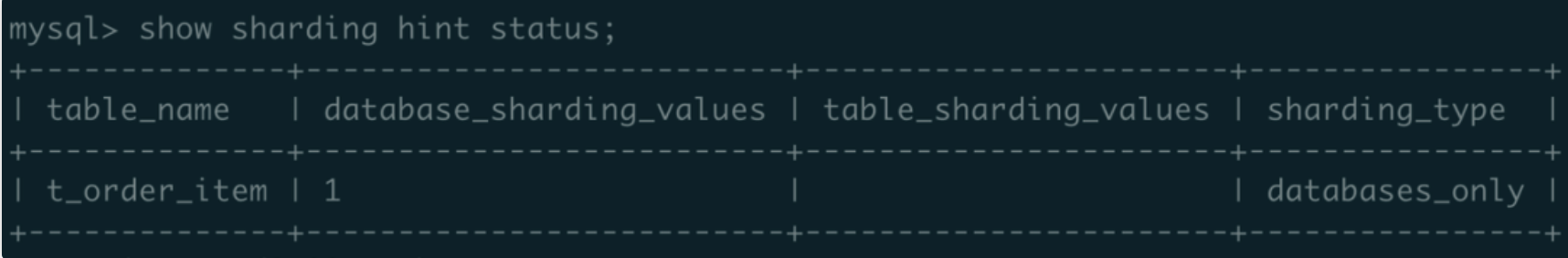
b. Execute show sharding hint status; show t_order_item’s database_sharding_values as 1. Update sharding_type value as databases_only.
c. Execute preview select * from t_order_item; SQL all hinted to ds_1:
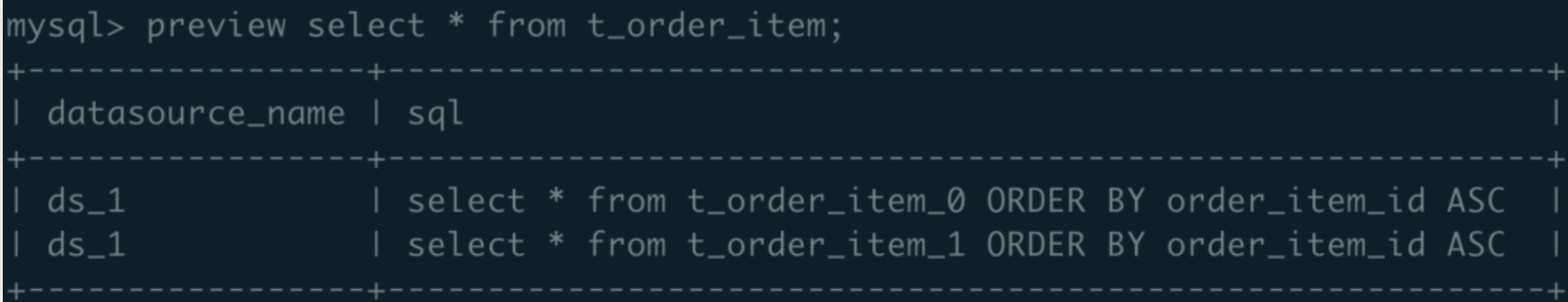
*Note: According to the sharding rules of YAML configuration, when database_value is an odd number, hint at ds_1; when database_value is an even number, hint at ds_0.
-add sharding hint database_value;
For the current connection only. Add
t_order_item’s database sharding value.
Input command
mysql> add sharding hint database_value t_order_item = 5;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Execute show sharding hint status; Show t_order_item’s database_sharding_values as 5; update sharding_type value as databases_tables;
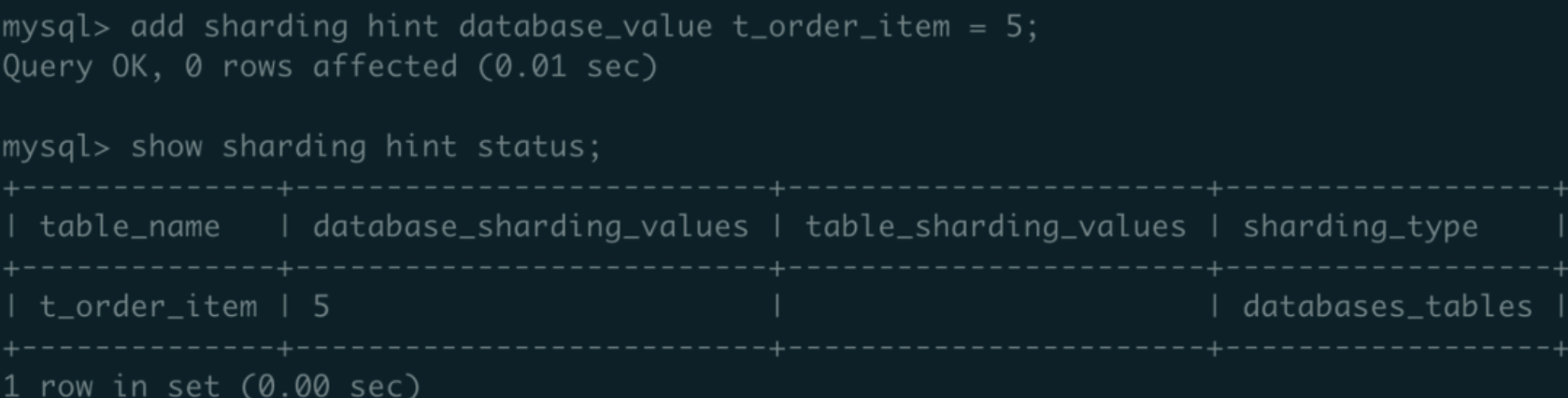
c. Execute preview select * from t_order_item; SQL commands are all hinted to ds_1:

Enter the add command again to add an even value.
mysql> add sharding hint database_value t_order_item = 10;
Output:
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Execute show sharding hint status; show t_order_item’s database_sharding_values = ‘5,10’:
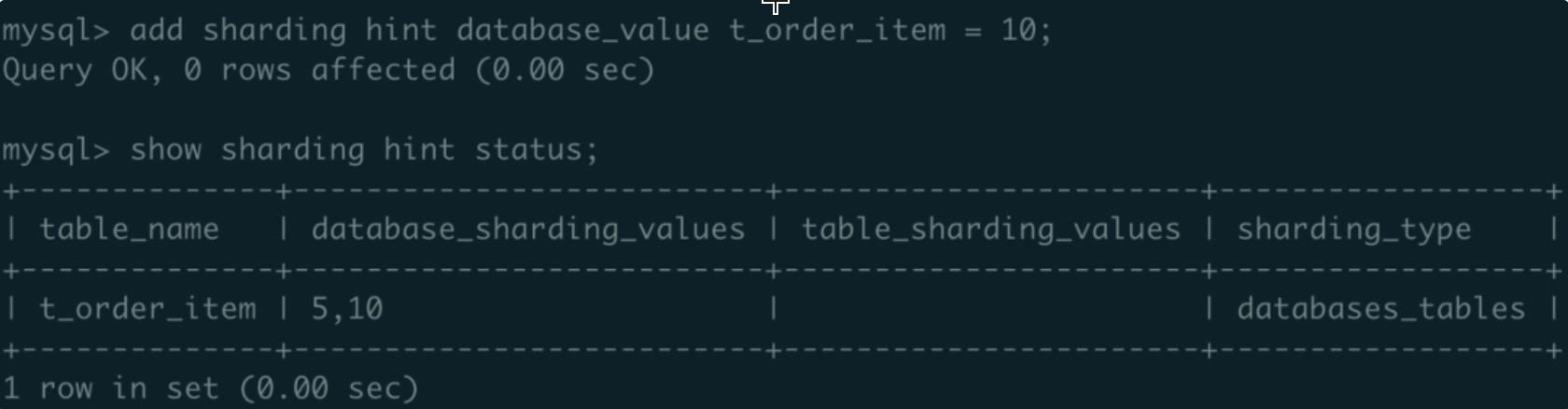
c. Execute preview select * from t_order_item; SQL hint contains ds_0 and ds_1: ( Because the hint values include both odd and even number so it contains all target data sources)
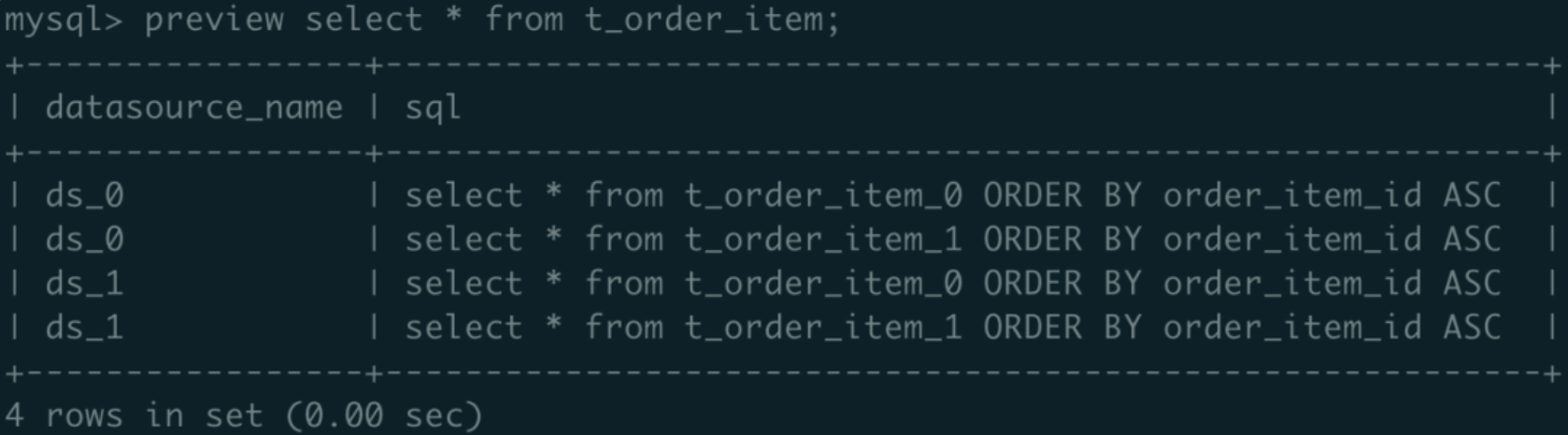
-add sharding hint table_value;
For the current connection only. Add database sharding value for
t_order_item.
Input command
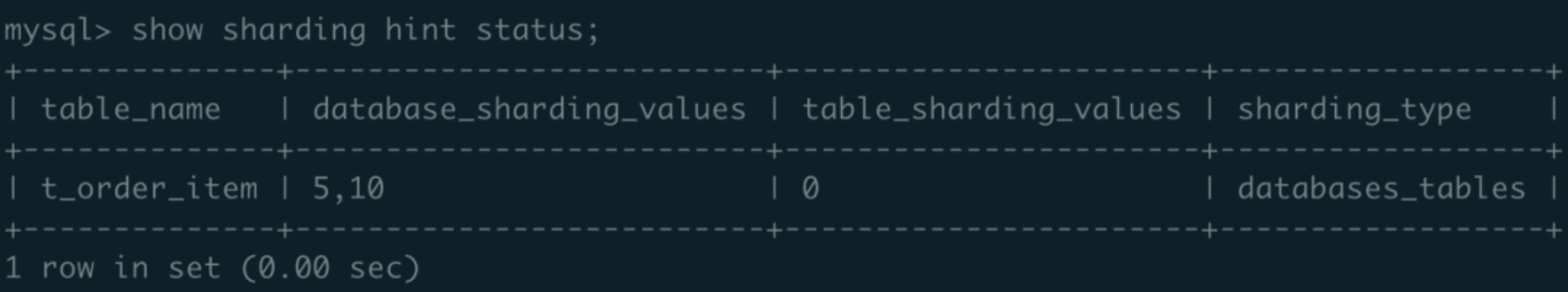
mysql> add sharding hint table_value t_order_item = 0;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Execute show sharding hint status; show t_order_item’s database_sharding_values as ‘5,10’ while table_sharding_values is ‘0’:
c. Execute preview select * from t_order_item; the Hint condition is shown in the figure below; Every database only queries t_order_item_0:
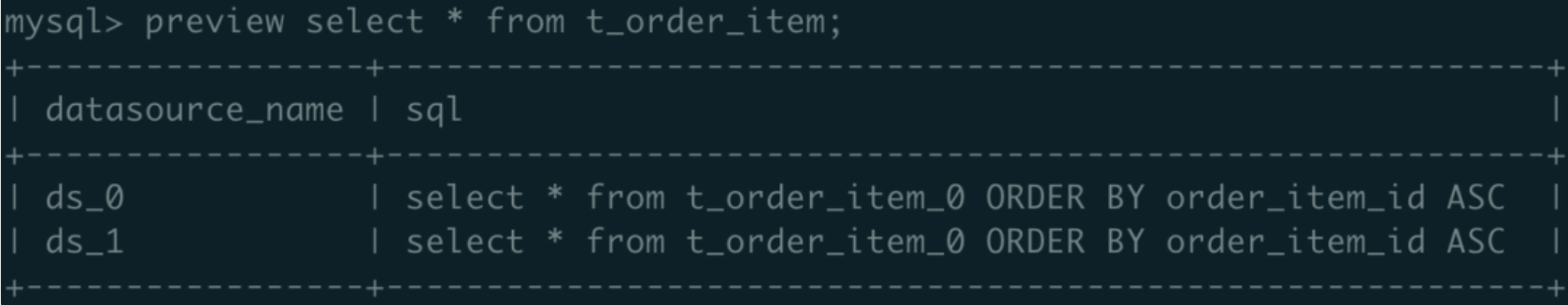
Note: According to the sharding rules of YAML configuration, when table_value is an odd number, hint t_order_item_1; when database_value is an even number, hint t_order_item_0.
It’s quite similar to add sharding hint database_value; you can set more than one hint values in add sharding hint database_value, to cover more shards.
clear sharding hint
For the current connection only. Clear sharding hint setting.
Input command
mysql> clear sharding hint;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Clear sharding hint and recover default; use show sharding hint status; to see the result. The initial status is:

clear hint
It is a special command because it contains the features of
clear readwrite_splitting hintandclear sharding hint. It can clear all hint values of read-write splitting and sharding. Use the command, and you will get the initial status.
Set hint value and then execute the command;
mysql> clear hint;
Output
a. If successful, show “Query OK, 0 rows affected”;
b. Get readwrite_splitting hint default and sharding hint default; use show readwrite_splitting hint status ; or show sharding hint status; command to see the result.
Note: Please remember: if you need to use DistSQL Hint, you need to enable the configurationproxy-hint-enabledof ShardingSphere-Proxy. For more information, please read:
https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-proxy/props/
There Are More Concerning RAL Commands
RAL not only contains all the SCTL functions, but also provides other useful administrational features including elastic scaling, instance ciruit-breaker, disabling read database for read-write splitting, etc.
For more details about RAL, please consult the relevant documentation: https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-proxy/distsql/syntax/ral/
Conclusion
That’s all folks. If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to comment on our GitHub Issues or Discussions sections. You’re welcome to submit your pull request and start contributing to the open source community, too. We’ve also set up a Slack channel, where you can connect with other members of our community and discuss technology with us.
Open Source Project Links:
ShardingSphere Github: https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere
ShardingSphere Twitter: https://twitter.com/ShardingSphere
ShardingSphere Slack Channel: https://join.slack.com/t/apacheshardingsphere/shared_invite/zt-sbdde7ie-SjDqo9~I4rYcR18bq0SYTg
GitHub Issues https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere/issues
Contributor Guide: https://shardingsphere.apache.org/community/cn/involved/
References
https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere/pull/1586
https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere/issues/11677
Authors
Jiang Longtao

SphereEx Middleware Development Engineer & Apache ShardingSphere Committer. Currently, he is in charge of DistSQL and permission control development.
Lan Chengxiang

SphereEx Middleware Development Engineer & Apache ShardingSphere Contributor. He focuses on DisSQL design and development.