Apache ShardingSphere Enterprise Applications
Apache ShardingSphere Enterprise Applications
To further understand application scenarios, enterprises’ needs, and improve dev teams’ understanding of Apache ShardingSphere, our community launched the “Enterprise Visits” series.
Keep
For our community’s first visit, we went to Asia’s leading workout & fitness trainer app maker “Keep” headquarters at Vanke Times Center, and shared our technologies with developers at Keep Co.
Way back in 2018, Keep had already deployed ShardingSphere capabilities such as sharding and read/write splitting in multiple application scenarios for its diversified lines of business.
With the release of Apache ShardingSphere 5.0, the concept of Database Plus and pluggable architecture has to some extent, reshaped the ShardingSphere ecosystem. During our visit, we conducted in-depth exchanges and discussions with our counterparts at Keep.

Keep engineers expressed great interest in Apache ShardingSphere 5.0. At the event, Juan Pan, Apache ShardingSphere PMC and SphereEx CTO, presented a full overview of the initial ShardingSphere architecture, user-end access, community building and the Database Plus concept.

Database Plus: Freeing DBAs and Developers
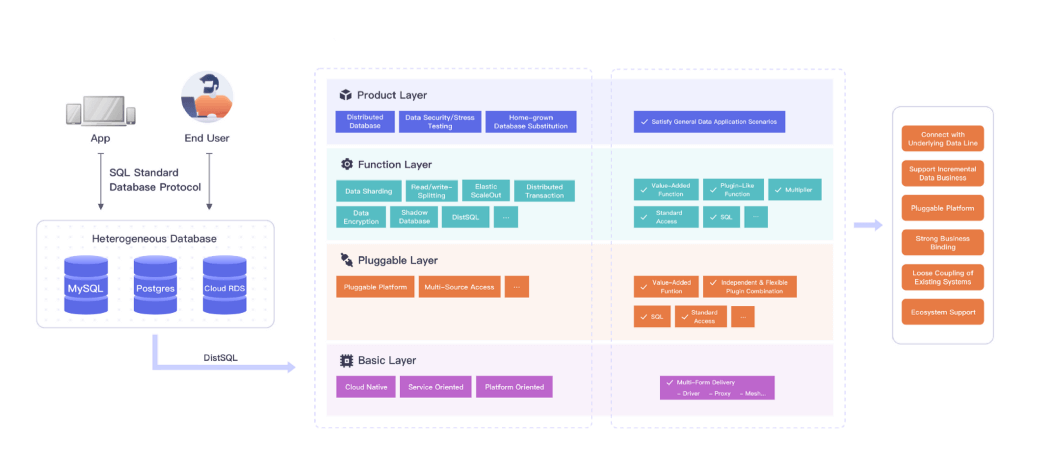
Database Plus is a design concept of the distributed database system. By building a standard layer and ecosystem for use and interaction above fragmented heterogeneous databases, and by multiplying and expanding computing capabilities (e.g. data sharding, data encryption and decryption), all the interaction between applications and databases is oriented to the standard layer built by Database Plus. This results in shielding the differentiated impact of database fragmentation on upper layer transactions.
Pan believes that the global database industry has boomed thanks in large to the following two reasons:
- Business side demand:
In terms of business, to ensure sustained visits and transactions growth, underlying databases must respond to requests as soon as possible. In addition, the breakup of microservices and subsequent modification of corresponding databases also generate demands from the business side.
- Operations & maintenance side demand:
DBAs are responsible for running the whole business and data system, including data security, backup, distributed governance, and API smart monitoring of data clusters.
If the middle layer can meet transaction traffic and understand the request, DBAs can modify the request accordingly and then more operations can be performed. Therefore, we need to strike a balance between the two sides of demand to carry transaction traffic and support database capacity building, thus creating an efficient, collaborative ecosystem between the two sides. Following the version 5.0 release, the sharding function is no longer at the core of Apache ShardingSphere. Actually, sharding has been “downgraded” to a secondary function in the ShardingSphere ecosystem. Following the Database Plus concept, Apache ShardingSphere has built a pluggable architecture ecosystem, enabling the middle layer to achieve more value-added capabilities.
Taking data encryption and decryption as an example, we can see how they are generally done at the business layer because MySQL and other databases do not support encrypted algorithms themselves. This means encryption & decryption is only be achievable at application and business layers. However, this poses a problem if we consider complex online businesses that face considerable tasks when they upgrade their encryption algorithms.
The best solution to this problem is to encrypt and decrypt data at the middle layer. ShardingSphere-Proxy can be directly bound to databases, be placed at the middle layer between applications and underlying databases. ShardingSphere-proxy will feel “DB-like” by taking advantage of protocols that are compatible with different databases, thus deciding which node the SQL quest will fall on, letting upper layer applications be programmed for ShardingSphere, and shielding the impact of underlying databases. Data is in plaintext status when the transaction sends a request, but it will be encrypted after going through Proxy and decrypted when being retrieved.
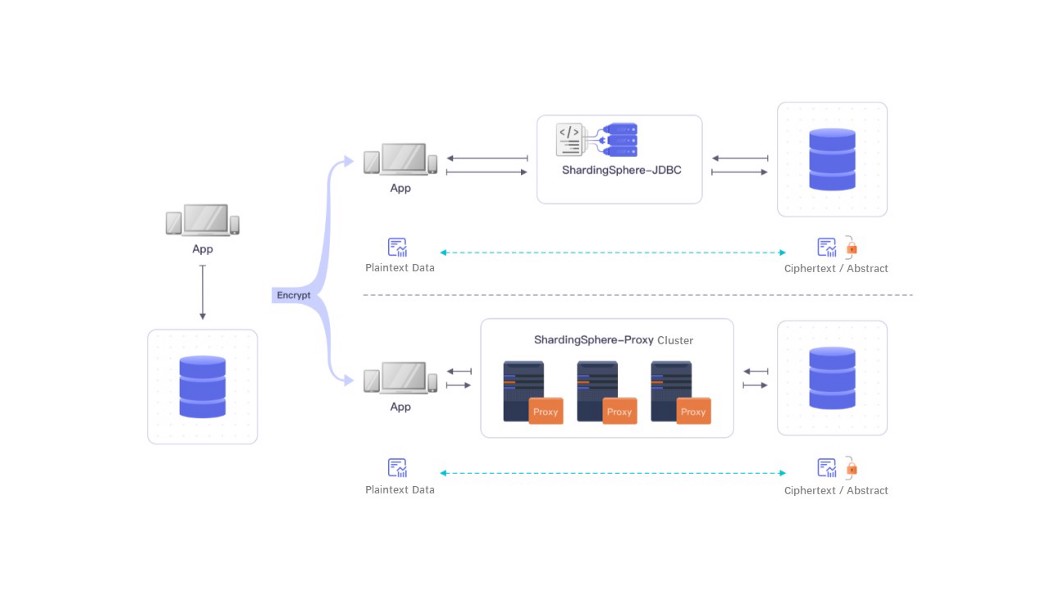
As such, the ShardingSphere encryption and decryption process can be separated from the existing system of applications and databases and can be linked with special encryption algorithms, especially in the cases where a cipher machine is involved. ShardingSphere capabilities such as encryption can free significant amounts of DBAs’ and developers’ time, allowing them to focus more on businesses.
iQiyi
Our second stop took us to the leading online streaming platform in Asia, iQiyi.
In November 2021, a team from the ShardingSphere community visited iQiyi the innovation center of iQiyi for in-depth interactions and discussions with their counterparts from Beijing and Shanghai. During the meetup, Zhang Liang, Apache ShardingSphere PMC Chair and SphereEx Founder, provided details on the latest Apache ShardingSphere community initiatives, its future development and Database Mesh.

During the meetup, iQiyi was especially interested in the capabilities and future plans of ShardingSphere and Database Mesh. here are some key takeaway questions from the visit:
- How does ShardingSphere manage its encryption keys?
Encryption key management is a capability subordinate to the encryption algorithm. When ShardingSphere needs an encryption key in its decryption, the key could be passed through properties configured by the encryption algorithm. In principle, encryption key management is not a capability of ShardingSphere but the job of the encryption algorithm.
- Is there a built-in cryptographic algorithm in ShardingSphere? Or is it done through outside cooperation?
Strictly speaking, ShardingSphere is not equipped with built-in capability. That’s because the pluggable architecture of ShardingSphere is divided into multiple layers, and the encryption module itself is only a capability of L2 of the pluggable architecture.
The encryption module only defines the top-layer encryption connector and the detailed encryption algorithm achieves the pluggable part of the connector. Currently, ShardingSphere supports several of the most commonly used open source algorithms, but it does not support any national cryptographic algorithm in particular.
Integrating an encryption algorithm is easy for developers: instead of changing source codes, all they need is a ShardingSphere encryption algorithm connector. ShardingSphere’s data encryption process is completely transparent to users and they very easy to use.
- What’s the future plan for Database Mesh and SphereEx?
Database Mesh is another ShardingSphere initiative. We are now planning to integrate Database Mesh through Sidecar. Sidecar will be used to manage traffic, while ShardingSphere will be used to manage to compute, and the underlying databases’ nodes to manage storage.
Sidecar’s and ShardingSphere functions overlap in part, but not completely. ShardingSphere has more than 190 modules, therefore it’s not possible to completely replace ShardingSphere with Sidecar. That’s why ShardingSphere empowers some lightweight capabilities to Sidecar, and Sidecar is equipped with the capabilities to buffer some traffic and requests.
The database computing capability is still processed by ShardingSphere, as it would consume too many application resources to run heavyweight computation via Sidecar for the distributed transaction, query and optimization of heterogeneous databases.
In the future, other Sidecar capabilities, such as management, SQL auditing and authorities, will be developed. In this way, Sidecar and ShardingSphere will have their own focuses, providing a better solution.
- Sidecar is equivalent to a data plane. Will you combine the control plane with Istio or will you build the control plane separately?
ShardingSphere uses DistSQL (Distributed SQL) to create rules for sharding, encryption and so on. ShardingSphere is already equipped with the control plane capability of Sidecar. Any capability achieved on Sidecar can be controlled by ShardingSphere’s DistSQL.
In the future, we will consider integrating Sidecar into the Istio ecosystem.
So far, Apache ShardingSphere with the release of a version of 5.0 has officiallyrepositioned itself in a new field with the Database Plus concept at its core. In addition to the powerful incremental capability at the upper layer of databases, the Database Plus architecture also opens a highly extensible database ecosystem to developers and users, charting a new future development course for Apache ShardingSphere.
Sohu
The third ShardingSphere community visit took us to Sohu — the advertising, search engine, online multiplayer gaming and other services’ giant.
The Apache ShardingSphere community team visited Sohu.com headquarters for in-depth discussions with their counterparts at the internet giant. At the meet-up, Juan Pan, Apache ShardingSphere PMC and SphereEx CTO, elaborated on Apache ShardingSphere’s capabilities.
Sohu, Inc., an integrated Internet company with a rich history and comprehensive lines of business, uses ShardingSphere products in their multiple lines of business, such as social media and video services.
Driven by ShardingSphere-JDBC and with ShardingSphere-Proxy as the container management platform, ShardingSphere provides support for Sohu in all aspects, helping Sohu relieve database traffic stress.
At the event, engineers from Sohu.com expressed great interest in Apache ShardingSphere 5.0. Juan Pan presented a full overview of ShardingSphere’s architecture, client end access, community building and the Database Plus concept.
Navigate & Solve Industry Challenges
Due to the complexity of enterprise database systems, and the heavy cost of databases, service providers are supposed to provide enterprises with mainstream database products as well as products and services that can meet multiple needs.
Facing diverse users' needs and increasingly diversified products in the database market, one viable solution could be database deployment and functions with higher flexibility and scalability.
By creating upper-level standards and ecosystems for heterogeneous databases, Apache ShardingSphere provides diversified functions that can precisely meet enterprise needs. As an ecosystem consisting of multiple adapters, by using a hybrid deployment model of ShardingSphere-JDBC and ShardingSphere-Proxy, Apache ShardingSphere enables users to configure sharding strategies through one console and to flexibly create application systems that suit the needs in different scenarios. This allows engineers more freedom to build system architectures that could best suit the needs of their ongoing projects.
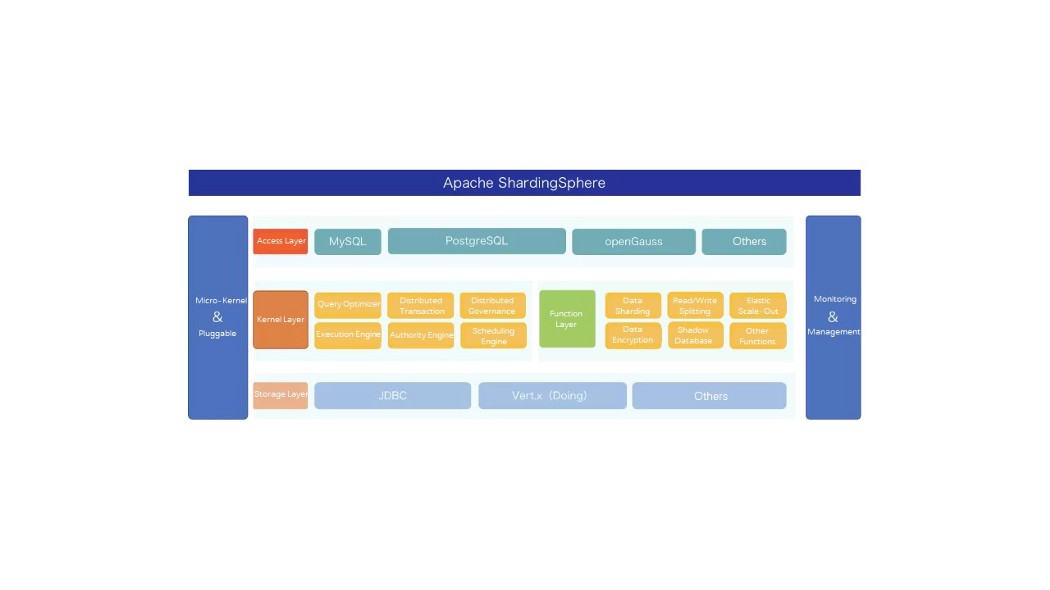
Centering around connections, incremental and pluggable features, and based on a pluggable architecture, Apache ShardingSphere creates a powerful kernel architecture in the form of micro-kernel.
Based on its powerful kernel capabilities, Apache ShardingSphere products can provide users with ideal solutions for distributed database, data security, database gateway and full-link stress testing, helping increase the efficiency of enterprises and users.
When it comes to future optimization, Pan believes that some deficiencies remain in Apache ShardingSphere’s performance and this is particularly true for ShardingSphere-Proxy’s adaptor. In the future, the community will double down on improving its kernel, minimizing business and data performance loss of the Proxy, improving routing and rewriting logic, reducing creating database objects, and avoiding excess young GC.
Apache ShardingSphere Open Source Project Links:
Author
Yacine Si Tayeb
SphereEx Head of International Operations
Apache ShardingSphere Contributor
Passionate about technology and innovation, Yacine moved to Beijing to pursue his Ph.D. in Business Administration, and fell in awe of the local startup and tech scene. His career path has so far been shaped by opportunities at the intersection of technology and business. Recently he took on a keen interest in the development of the ShardingSphere database middleware ecosystem and Open-Source community building.
