Apache ShardingSphere is an ecosystem to transform any database into a distributed database system, and enhance it with sharding, elastic scaling, encryption features & more.
The project is committed to providing a multi-source heterogeneous, enhanced database platform and further building an ecosystem around the upper layer of the platform. Database Plus, the design philosophy of Apache ShardingSphere, aims at building the standard and ecosystem on the upper layer of the heterogeneous database. It focuses on how to make full and reasonable use of the computing and storage capabilities of existing databases rather than creating a brand new database. It attaches greater importance to the collaboration between multiple databases instead of the database itself.
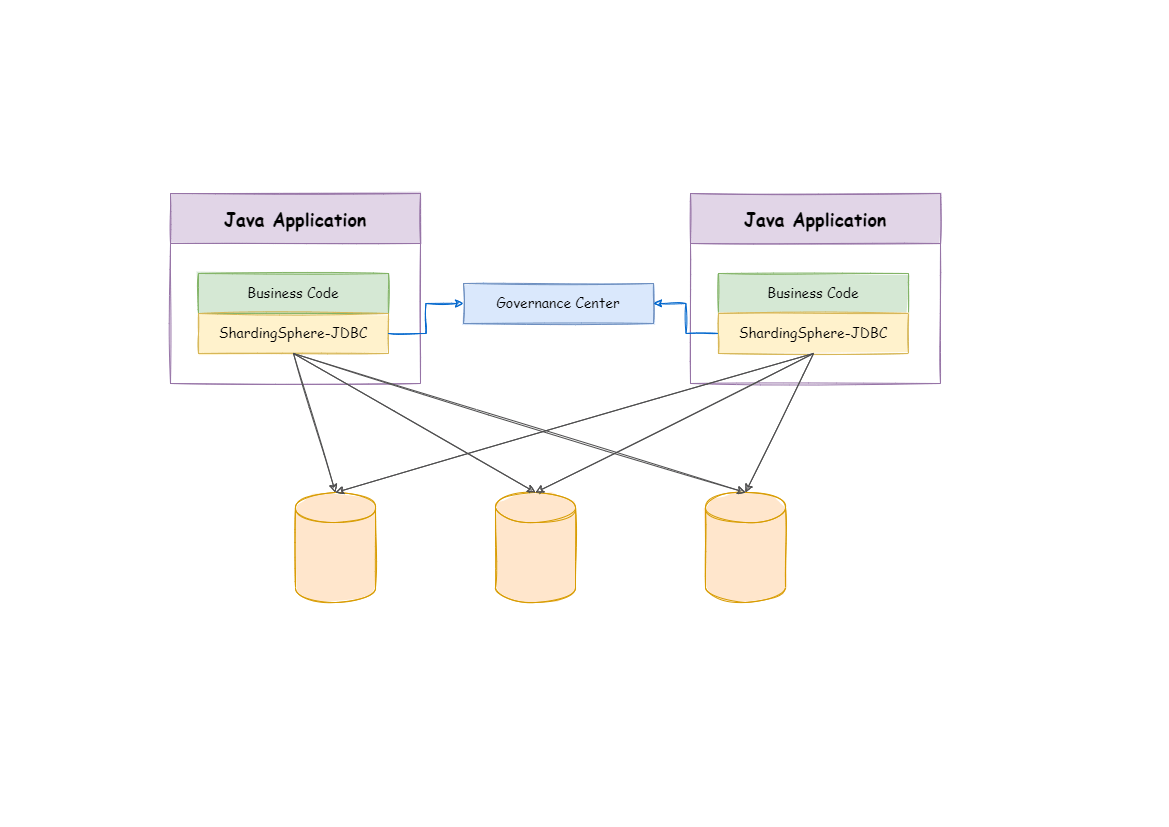
ShardingSphere-JDBC is a lightweight Java framework that provides additional services at Java’s JDBC layer.
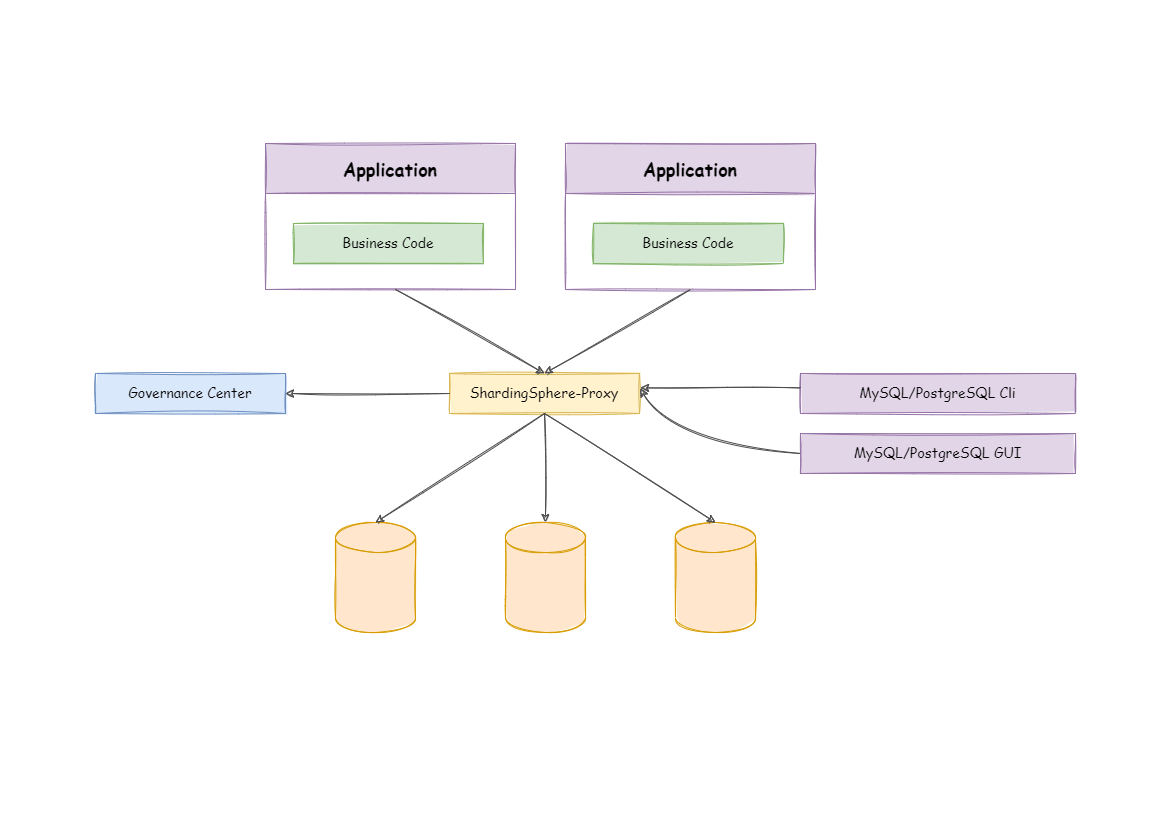
ShardingSphere-Proxy is a transparent database proxy, providing a database server that encapsulates database binary protocol to support heterogeneous languages.
| Feature | Definition |
|---|---|
| Data Sharding | Data sharding is an effective way to deal with massive data storage and computing. ShardingSphere provides a distributed database solution based on the underlying database, which can scale computing and storage horizontally. |
| Distributed Transaction | Transactional capability is key to ensuring database integrity and security and is also one of the databases' core technologies. With a hybrid engine based on XA and BASE transactions, ShardingSphere provides distributed transaction capabilities on top of standalone databases, enabling data security across underlying data sources. |
| Read/write Splitting | Read/write splitting can be used to cope with business access with high stress. ShardingSphere provides flexible read/write splitting capabilities and can achieve read access load balancing based on the understanding of SQL semantics and the ability to perceive the underlying database topology. |
| Data Migration | Data migration is the key to connecting data ecosystems. ShardingSphere provides migration capabilities to help users migrate the data from other data sources, while simultaneously performing data sharding. |
| Query Federation | Federated queries are effective in utilizing data in a complex data environment. ShardingSphere provides complex data query and analysis capabilities across data sources, simplifying the data aggregation from different data locations. |
| Data Encryption | Data Encryption is a basic way to ensure data security. ShardingSphere provides a complete, transparent, secure, and low-cost data encryption solution. |
| Shadow Database | In full-link online load testing scenarios, ShardingSphere supports data isolation in complex load testing scenarios through the shadow database function. Execute your load testing scenarios in a production environment without worrying about test data polluting your production data. |
Having been polished for years, the driver is close to a native JDBC in terms of efficiency, with ultimate performance.
The proxy can be accessed by any application using MySQL/PostgreSQL protocol, and the driver can connect to any database that implements JDBC specifications.
In response to database switchover scenarios, ShardingSphere can achieve smooth business migration without business intrusion.
ShardingSphere offers a flat learning curve to DBAs and is interaction-friendly while allowing the original technology stack to remain unchanged.
It can provide enhancement capability based on mature databases while ensuring security and stability.
It supports computing, storage, and smooth online expansion, which can meet diverse business needs.
It can provide users with flexibility thanks to custom systems based on multi-level (kernel, feature, and ecosystem) plugin capabilities.
ShardingSphere adopts the database plus design philosophy, which is committed to building the standards and ecology of the upper layer of the database and supplementing the missing capabilities of the database in the ecology.
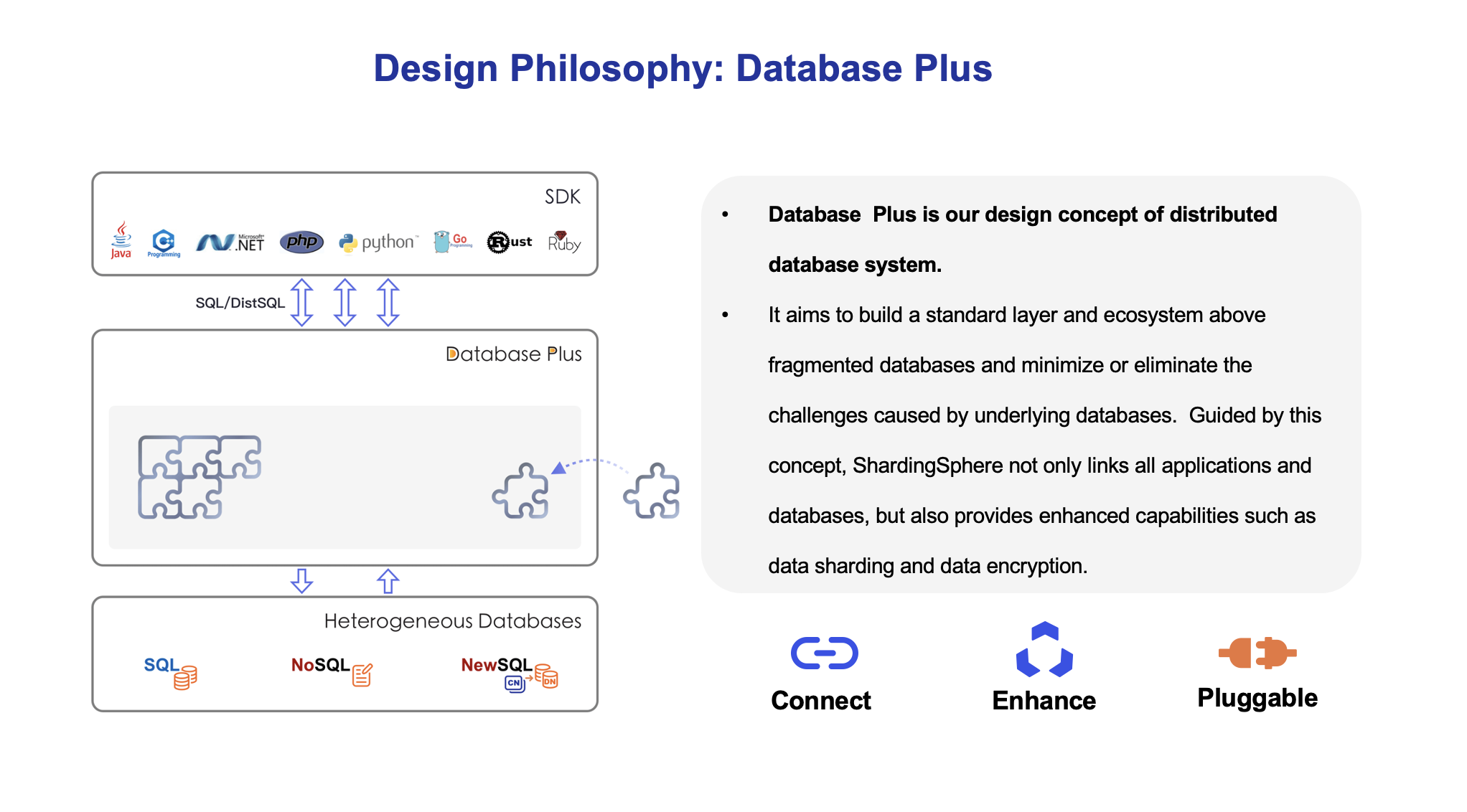
Through flexible adaptation of database protocols, SQL dialects, and database storage, it can quickly build standards on top of multi-modal heterogeneous databases, while providing standardized connection mode for applications through built-in DistSQL.
It can further provide distributed capabilities and traffic enhancement functions based on native database capabilities. The former can break through the bottleneck of the underlying database in computing and storage, while the latter provides more diversified data application enhancement capabilities through traffic deformation, redirection, governance, authentication, and analysis.
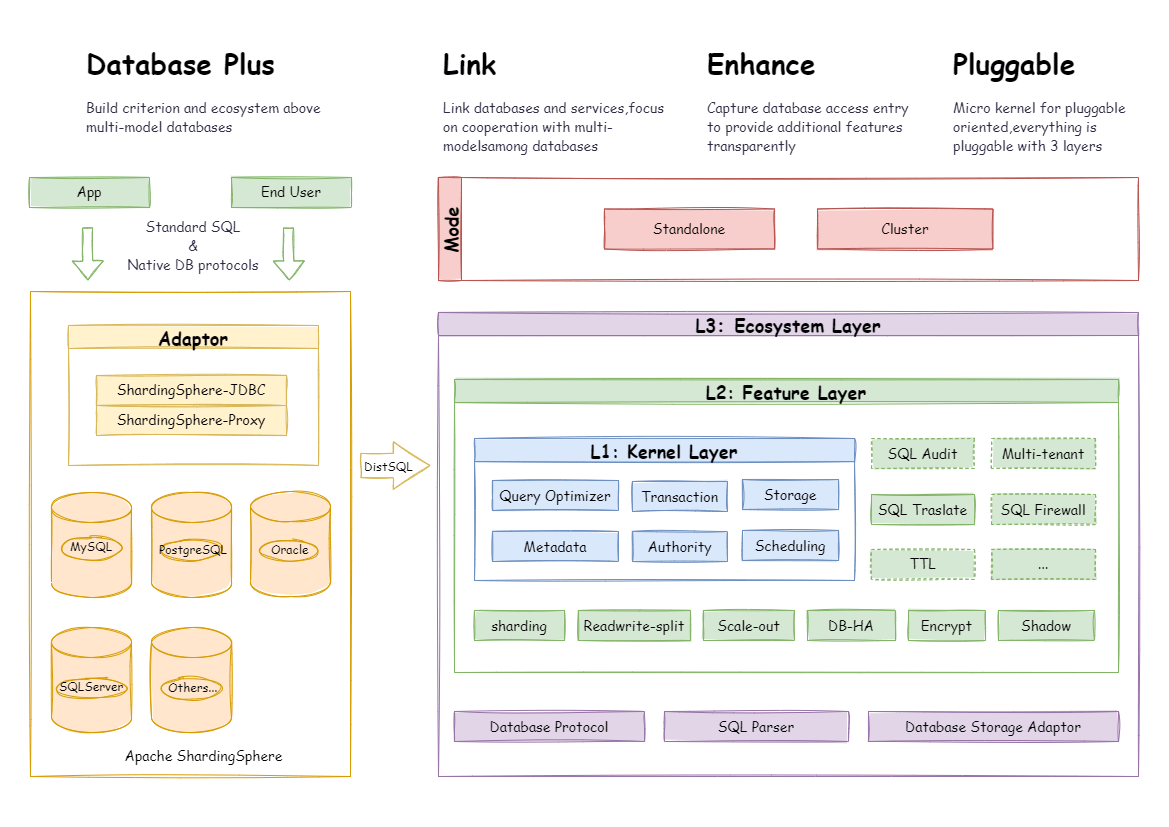
The pluggable architecture of Apache ShardingSphere is composed of three layers - L1 Kernel Layer, L2 Feature Layer and L3 Ecosystem Layer.
An abstraction of databases' basic capabilities. All the components are required and the specific implementation method can be replaced thanks to plugins. It includes a query optimizer, distributed transaction engine, distributed execution engine, permission engine and scheduling engine.
Used to provide enhancement capabilities. All components are optional, allowing you to choose whether to include zero or multiple components. Components are isolated from each other, and multiple components can be used together by overlaying. It includes data sharding, read/write splitting, data encryption and shadow database and so on. The user-defined feature can be fully customized and extended for the top-level interface defined by Apache ShardingSphere without changing kernel codes.
It is used to integrate and merge the current database ecosystems. The ecosystem layer includes database protocol, SQL parser and storage adapter, corresponding to the way in which Apache ShardingSphere provides services by database protocol, the way in which SQL dialect operates data, and the database type that interacts with storage nodes.
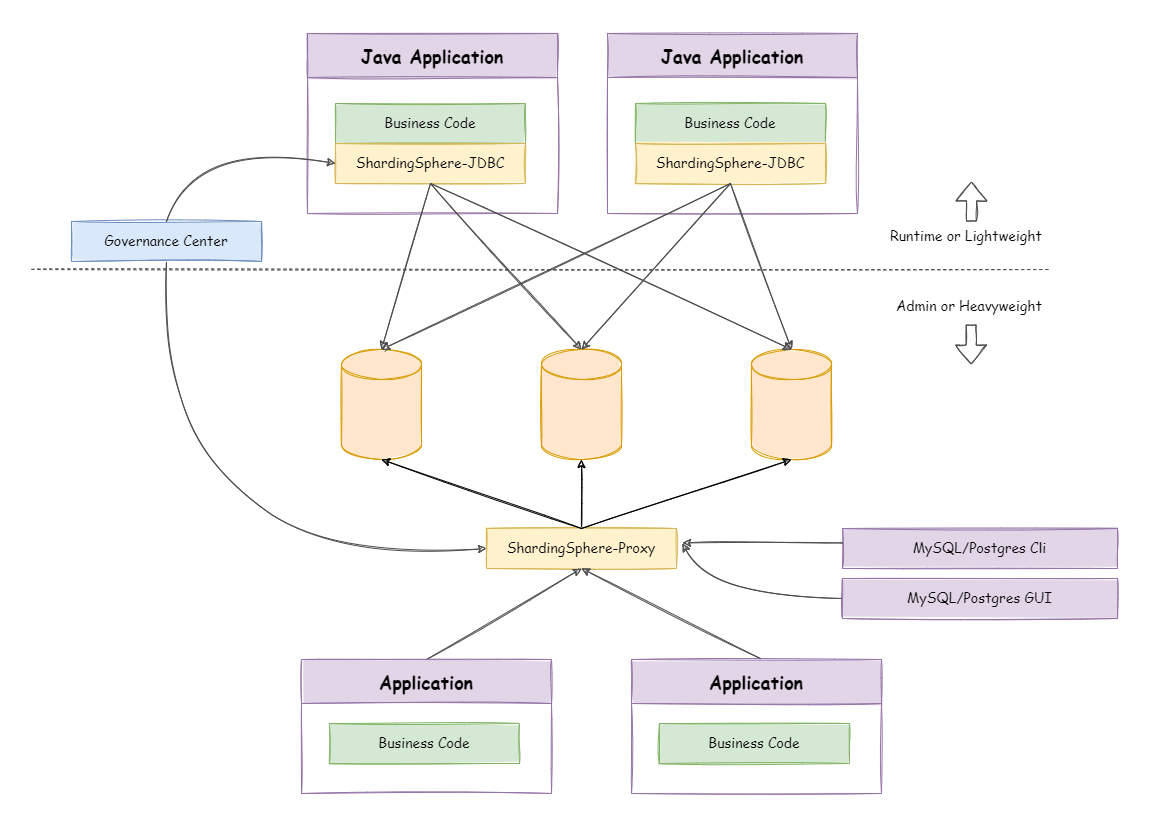
Apache ShardingSphere includes two independent clients: ShardingSphere-JDBC & ShardingSphere-Proxy. They all provide functions of data scale-out, distributed transaction and distributed governance, applicable in a variety of scenarios such as Java isomorphism, heterogeneous languages, and a cloud-native environment.
ShardingSphere-JDBC is a lightweight Java framework that provides additional services at Java’s JDBC layer. With the client connecting directly to the database, it provides services in the form of jar and requires no extra deployment and dependence. It can be considered as an enhanced version of the JDBC driver, which is fully compatible with JDBC and all kinds of ORM frameworks.
| ShardingSphere-JDBC | ShardingSphere-Proxy | |
|---|---|---|
| Database | Any |
MySQL/PostgreSQL |
| Connections Count Cost | More |
Less |
| Heterogeneous language | Java Only |
Any |
| Performance | Low loss |
Relatively High loss |
| Decentralization | Yes |
No |
| Static entry | No |
Yes |
ShardingSphere-Proxy is a transparent database proxy, providing a database server that encapsulates database binary protocol to support heterogeneous languages. Currently, MySQL and PostgreSQL protocols are provided. It can use any kind of terminal that is compatible with MySQL or PostgreSQL protocol to operate data, which is more friendly to DBAs.
| ShardingSphere-JDBC | ShardingSphere-Proxy | |
|---|---|---|
| Database | Any | MySQL/PostgreSQL |
| Connections Count Cost | More | Less |
| Heterogeneous language | Java Only | Any |
| Performance | Low loss | Relatively High loss |
| Decentralization | Yes | No |
| Static entry | No | Yes |
ShardingSphere-JDBC adopts a decentralized architecture, applicable to high-performance light-weight OLTP applications developed with Java. ShardingSphere-Proxy provides static entry and supports all languages, applicable to OLAP applications and the sharding databases management and operation situation.
Apache ShardingSphere is an ecosystem composed of multiple access ports. By combining ShardingSphere-JDBC and ShardingSphere-Proxy, and using the same registry to configure sharding strategies, it can flexibly build application systems for various scenarios, allowing architects to freely adjust the system architecture according to the current businesses.
Apache ShardingSphere provides two running modes: standalone mode and cluster mode.
It can achieve data persistence in terms of metadata information such as data sources and rules, but it is not able to synchronize metadata to multiple Apache ShardingSphere instances or be aware of each other in a cluster environment. Updating metadata through one instance causes inconsistencies in other instances because they cannot get the latest metadata.
It is ideal for engineers to build a ShardingSphere environment locally.
It provides metadata sharing between multiple Apache ShardingSphere instances and the capability to coordinate states in distributed scenarios.
It provides the capabilities necessary for distributed systems, such as horizontal scaling of computing capability and high availability. Clustered environments need to store metadata and coordinate nodes' status through a separately deployed registry center.
We suggest using cluster mode in production environment.
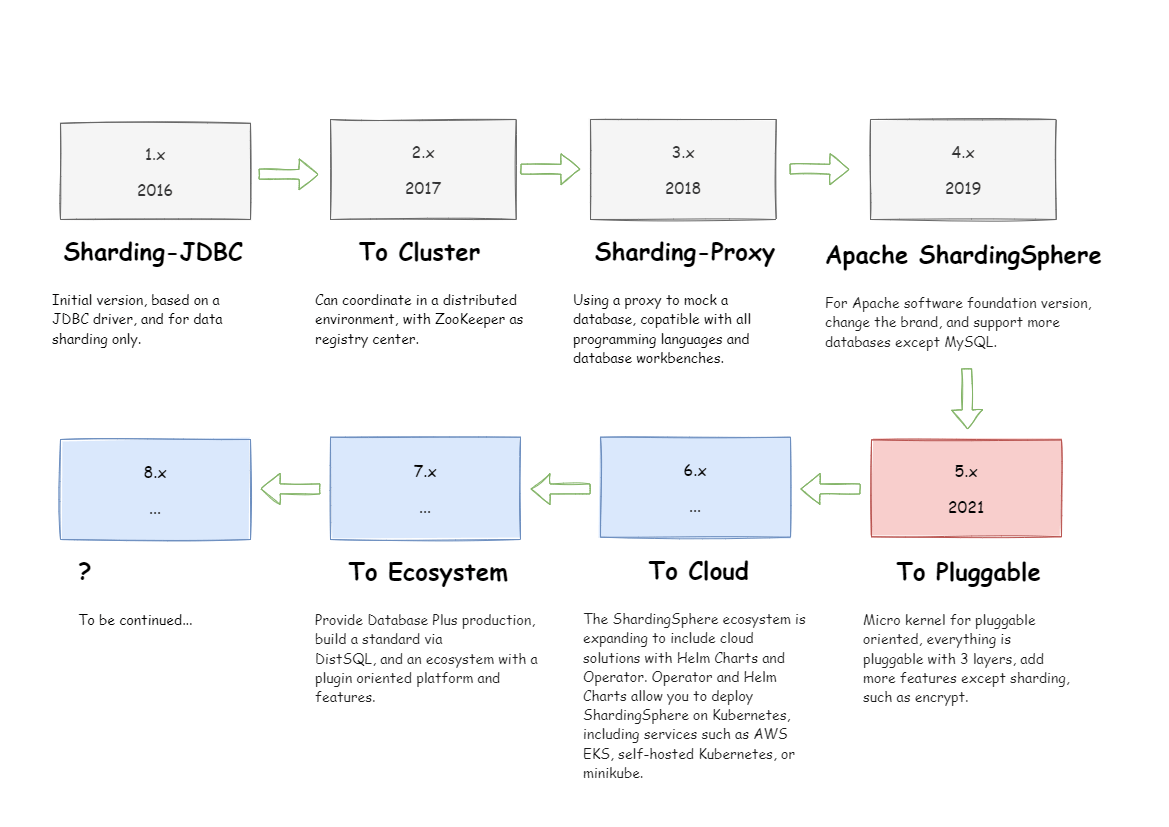
ShardingSphere became an Apache Top-Level Project on April 16, 2020. You are welcome to check out the mailing list and discuss via mail.




