Domain Model Configuration
This section explains configuration domain models in Sharding-JDBC. The following class diagram is about those domain models in Sharding-JDBC.
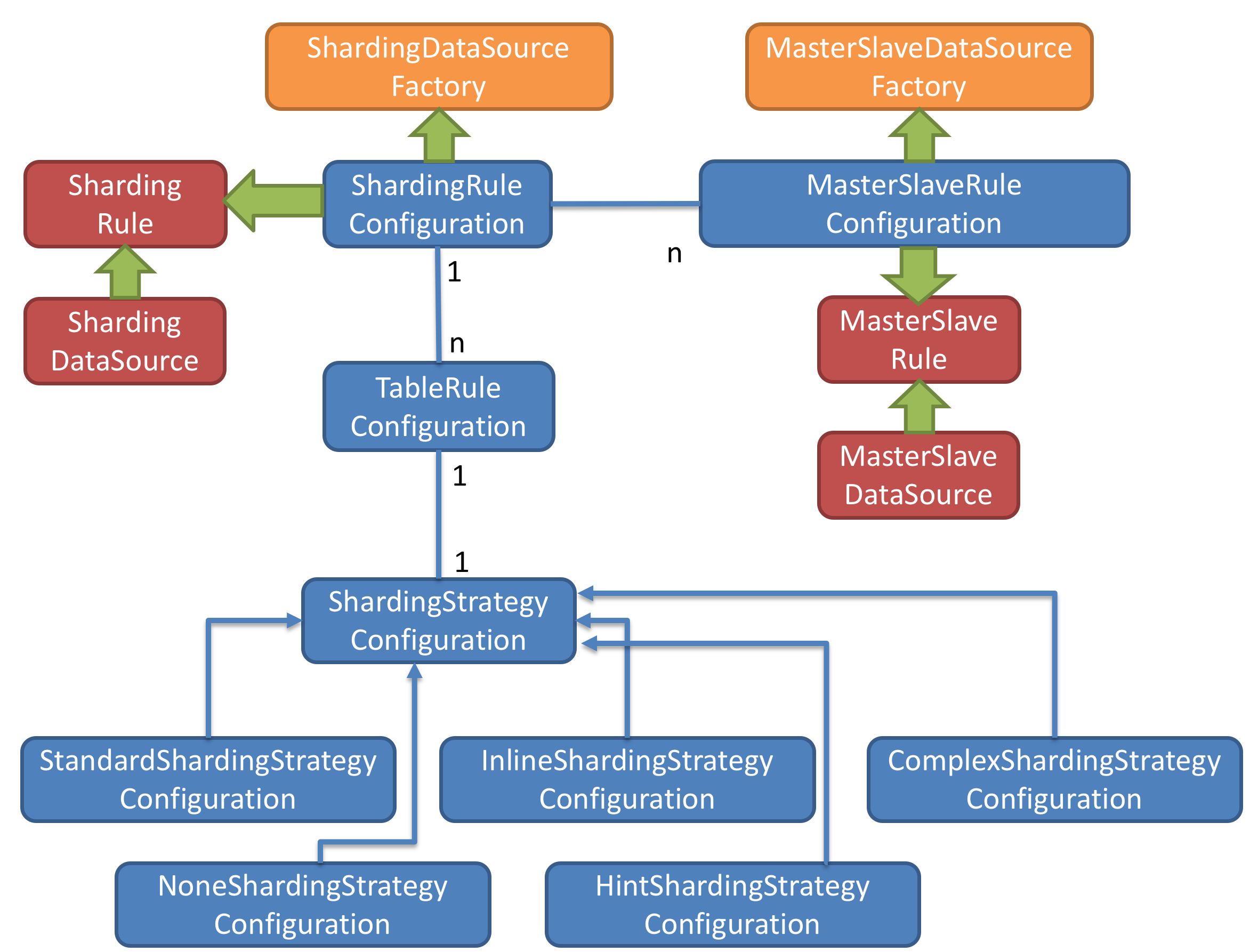
The Factory Method Pattern
The yellow part of the figure represents the Sharding-JDBC entry API, which is provided in the form of factory methods. It includes ShardingDataSourceFactory factory class and MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory factory class. ShardingDataSourceFactory is used to create JDBC driver for Sharding + Read-write splitting, but MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory is to create JDBC driver only for Read-write splitting.
Configuration Object
The blue part of the figure shows the sharding-jdbc configuration objects. ShardingRuleConfiguration is the entrance to configure the Sharding strategy, and it can include multiple TableRuleConfiguration and MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration. A TableRuleConfiguration is configured for a group of tables with the same sharding strategy. If both Sharding and Read-write splitting are used, you need to set MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration for each logic database used to do Read-write splitting. There is one-to-one correspondence between each TableRuleConfiguration and each ShardingStrategyConfiguration which consists of 5 kinds of strategies to choose from. For details on the use of sharding strategies, please read the Database Sharding.
MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration is only used for Read-write splitting.
Internal Object
The red part of the figure represents internal objects, which are used by Sharding-JDBC itself. Therefore users do not look inside those objects. By using ShardingRuleConfiguration and MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration, Sharding-JDBC provides final rules to ShardingDataSource and MasterSlaveDataSource which implement the DataSource interface.
Operation Steps
- Create Configuration object.
- The Configuration object is transformed into the Rule object through the Factory object.
- The Rule object is bound to the DataSource object through the Factory object.
- Sharding-JDBC operates Sharding and Read-write splitting on DataSource object.