Brief Introduction
Sharding-JDBC directly encapsulates the JDBC API,can be understood as a enhanced version of the JDBC driver, migrate legacy code almost zero costs:
- Suitable for any java ORM frameworks, such as: JPA, Hibernate, Mybatis or JDBC directly.
- Suitable for any database connection pool, such as: DBCP, C3P0, BoneCP, etc.
- In theory, any database that implements the JDBC specification can be supported.Support MySQL, Oracle, SQLServer and PostgreSQL.
Sharding-JDBC is a lightweight java framework, using the java-jdbc-client to connect database, providing services all-in-jar, no middle layer is used, no other dependence, DBA also don’t need to change the original dev mode.Use the “semi-understand” concept of SQL parsing engine to achieve maximum performance and compatibility.
The function of sharding-jdbc is flexible and comprehensive:
- Flexible sharding strategy, which support =, BETWEEN, IN, multiple sharding-columns and customized sharding strategy.
- Perfect SQL parsing,which supports aggregation, grouping, sorting, LIMIT, TOP and other queries, and supports cascading tables and Cartesian product table queries.
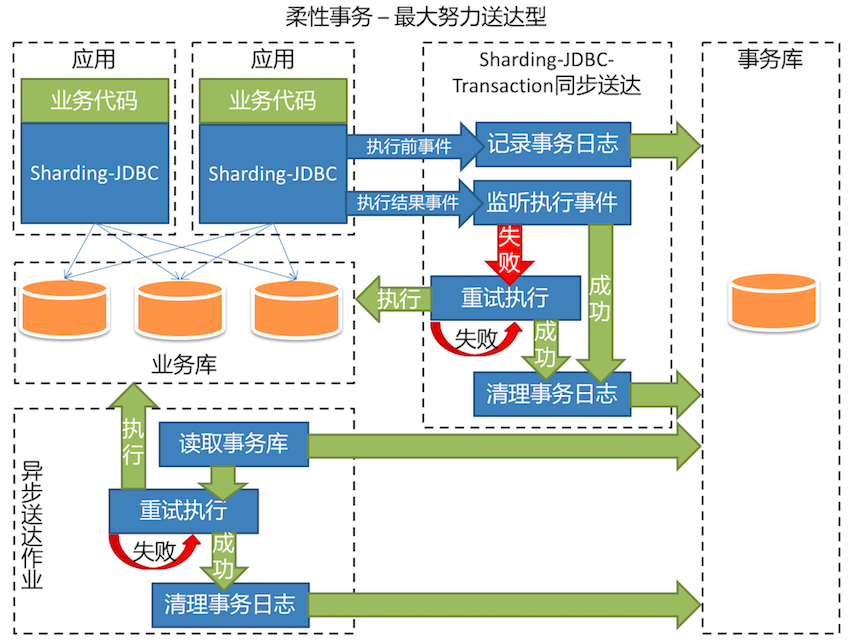
- Support B.A.S.E Transaction(Now only support Best Effort Delivery).
- Support Read/Write Splitting.
- Support Distributed Global Primary Key Generator.
Flexible And Diverse Configurations:
- Support Java and YAML
- Support user-defined Spring Namespace and Spring boot starter
- Flexible And Diverse Inline Expression
Distributed Governance Capability(2.0 New Feature)
- Configuration is centralized and dynamic,support dynamically switching of datasources, tables and sharding policies(2.0.0.M1)
- Client database governance, datasource automatic switching when failure(2.0.0.M2)
- Information Output based on Open Tracing protocol(2.0.0.M3)
Overall Architecture Diagram
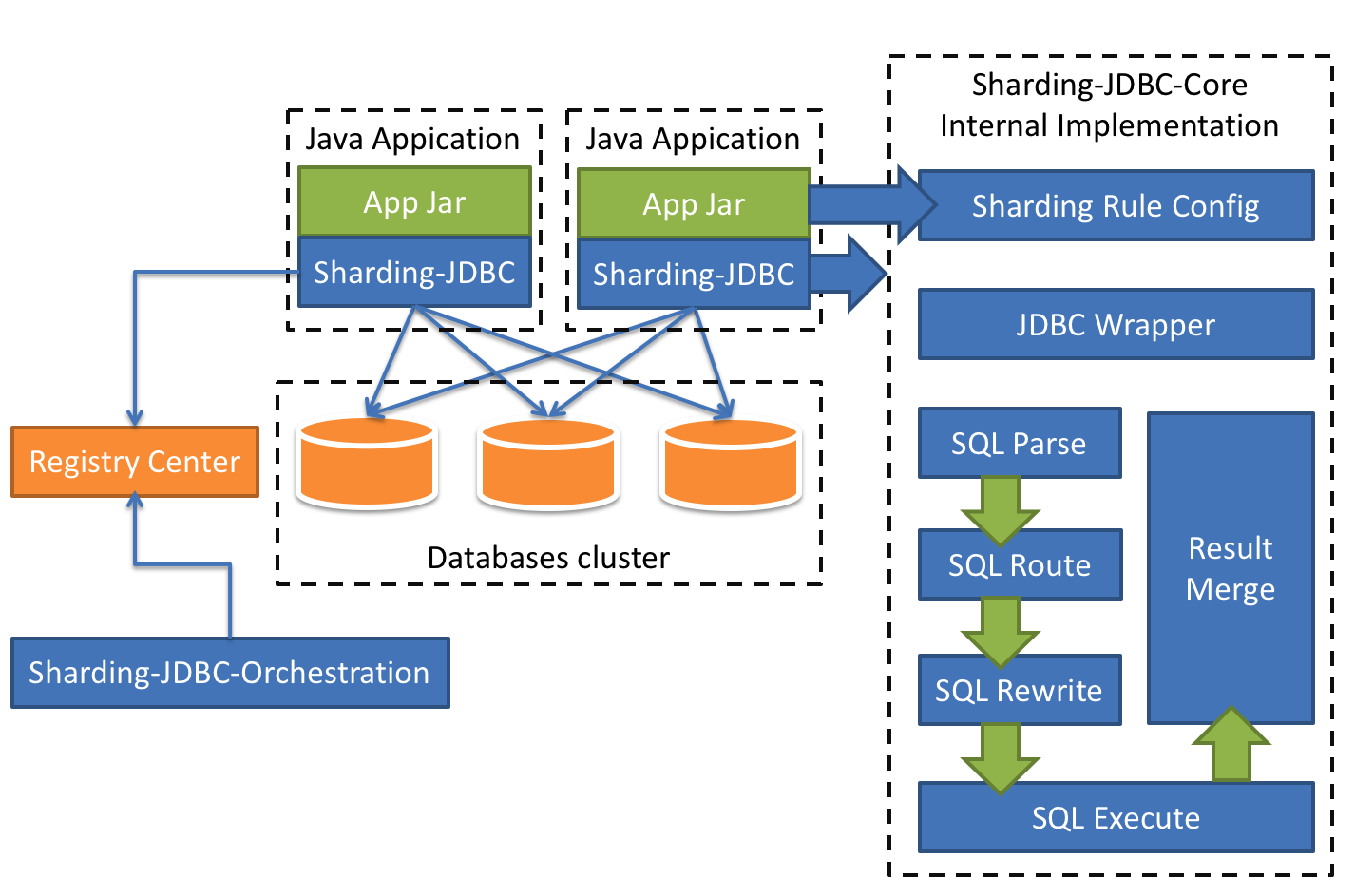
Quick start
Add maven dependency
<!-- add sharding-jdbc core module -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.shardingjdbc</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-core</artifactId>
<version>${latest.release.version}</version>
</dependency>
Rule configuration
Sharding Databases and tables is described by rule configuration,the following example is based on sharding databases by mod of user_id, and the configuration of the two databases and two tables is based on the mod of order_id.
You can configure it in Java code:
// Config the real datasource
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
// Config the first datasource
BasicDataSource dataSource1 = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource1.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource1.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0");
dataSource1.setUsername("root");
dataSource1.setPassword("");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_0", dataSource1);
// Config the second datasource
BasicDataSource dataSource2 = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource2.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource2.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1");
dataSource2.setUsername("root");
dataSource2.setPassword("");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_1", dataSource2);
// Config Table Rule Of Order
TableRuleConfiguration orderTableRuleConfig = new TableRuleConfiguration();
orderTableRuleConfig.setLogicTable("t_order");
orderTableRuleConfig.setActualDataNodes("ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}");
// Config sharding database strategy
orderTableRuleConfig.setDatabaseShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("user_id", "ds_${user_id % 2}"));
// Config sharding table strategy
orderTableRuleConfig.setTableShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("order_id", "t_order_${order_id % 2}"));
// Config data-swarding rule
ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfig = new ShardingRuleConfiguration();
shardingRuleConfig.getTableRuleConfigs().add(orderTableRuleConfig);
// Omit the configuration of order_item table rules...
// get datasource object
DataSource dataSource = ShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap, shardingRuleConfig, new ConcurrentHashMap(), new Properties());
Or configured by YAML, equivalent to the above configuration:
dataSources:
ds_0: !!org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0
username: root
password:
ds_1: !!org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
username: root
password:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}
databaseStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: user_id
algorithmInlineExpression: ds_${user_id % 2}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmInlineExpression: t_order_${order_id % 2}
t_order_item:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}
databaseStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: user_id
algorithmInlineExpression: ds_${user_id % 2}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmInlineExpression: t_order_item_${order_id % 2}
DataSource dataSource = ShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(yamlFile);
Rule configuration includes datasource configuration, table rule configuration, sharding database strategy, and sharding table strategy.This is just the simplest way of configuring,practical use can be more flexible, for example:Read/Write Splitting,multi sharding key,default sharding rule,distributed primary key,Cascading table bindings, etc.
Use Native JDBC INTERFACES
Get ShardingDataSource through ShardingDataSourceFactory factory and rule configuration , ShardingDataSource implements the JDBC DataSource standard interface.Then you can choose to use native JDBC to develop with DataSource, or use JPA, MyBatis, and other ORM tools. Take the JDBC native implementation as an example:
DataSource dataSource = ShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap, shardingRuleConfig);
String sql = "SELECT i.* FROM t_order o JOIN t_order_item i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.user_id=? AND o.order_id=?";
try (
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10);
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 1001);
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1));
System.out.println(rs.getInt(2));
}
}
}
Use Spring namespace configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:sharding="http://shardingsphere.io/schema/shardingjdbc/sharding"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://shardingsphere.io/schema/shardingjdbc/sharding
http://shardingsphere.io/schema/shardingjdbc/sharding/sharding.xsd
">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:conf/conf.properties" ignore-unresolvable="true" />
<bean id="ds_0" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="" />
</bean>
<bean id="ds_1" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="" />
</bean>
<sharding:inline-strategy id="databaseStrategy" sharding-column="user_id" algorithm-expression="ds_${user_id % 2}" />
<sharding:inline-strategy id="orderTableStrategy" sharding-column="order_id" algorithm-expression="t_order_${order_id % 2}" />
<sharding:inline-strategy id="orderItemTableStrategy" sharding-column="order_id" algorithm-expression="t_order_item_${order_id % 2}" />
<sharding:data-source id="shardingDataSource">
<sharding:sharding-rule data-source-names="ds_0,ds_1">
<sharding:table-rules>
<sharding:table-rule logic-table="t_order" actual-data-nodes="ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}" database-strategy-ref="databaseStrategy" table-strategy-ref="orderTableStrategy" />
<sharding:table-rule logic-table="t_order_item" actual-data-nodes="ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}" database-strategy-ref="databaseStrategy" table-strategy-ref="orderItemTableStrategy" />
</sharding:table-rules>
</sharding:sharding-rule>
</sharding:data-source>
</beans>